As email is one of the most integral ways to communicate digitally. With the increase in the use of emails and the trust, people have in emails. However, email scams are becoming a very common way to distract people. These scams are known as “email spoofing.” These spoof emails look legit, but unfortunately, they are not, as they make the recipient believe that the message originates from a trusted source. In simple words, email spoofing is a technique used by people with criminal mindsets to disguise their identity by forging the sender’s email address.
In this blog, we will explore everything related to email spoofing, such as what email spoofing is, how it works, how you can protect yourself against it, and much more. Let’s get started!
What is Email Spoofing?
Email spoofing is a type of cyberattack where the attacker sends an email with a false email header. The email header contains information about the sender, recipient, and subject line of the email. The subject of the spoof email looks so appealing that the recipient thinks that the email is sent by a trusted entity. Email spoofing is a tool of a phishing attack whose ultimate goal is to:
- Steal your information
- Steal your funds
- Get access to your online accounts
- Attach malware or virus to corrupt your device
According to spam statistics, about 85% of the total emails are spam, and most of the spoofed emails are easy to create and easy to catch, yet some of the malicious and targeted emails are not easy to catch, and they can be a huge security threat.
The moment you open a spoof email, the next moment, your information is no longer yours.

How Email Spoofing Works?
Scammers use the Simple Message Transfer Protocol (SMTP) specifically to start email spoofing. An SMTP server is generally used by email systems to send or receive emails. The weak point of the protocol is that it lacks a mechanism to authenticate the email addresses. This is the point at which scammers and fraudsters take advantage and send spoof emails.
What they do is, to make their spoofing emails appear to be authentic and true emails from the individual or entity they’re pretending to be, they forge email headers to make an email appear legit and they often modify the email components such as
- To
- From
- IP address
- Return-Path email addresses
But, in reality, they are just spoofing email addresses. They often use popular email services like Gmail, Outlook, and Office 365 to conduct email spoofing attacks.
This is not finished here! Scammers are well aware of phishing techniques and send a spoof email that looks like it is real but contains a link to a spoofing website, which is to steal your valuable information.
One of the most common attack that involves email spoofing is CEO fraud, also referred to as business email compromise (BEC). In this attack, the fraudster tricks the recipient by claiming to be an owner or CEO of the company and gives them some piece of information or transfer money so they believe the email is legit. This attack is mostly pitched for people working in the financial, accounts departments.
Types of Spoofing
Let’s discuss some other types of email spoofing attacks that scammers use:
IP spoofing
With this form of attack, the attacker modifies their IP address to make it seem as though the email was sent from an alternate source.
DNS spoofing
With this kind of attack, the perpetrator sets up a fake DNS server to lead the recipient to a fraudulent website while making the recipient believe that the email came from a reputable sender.
Display Name Spoofing
With this kind of spoofing, attackers change their display name to a trusted name or organization while still using a spoofed email address. The fact that the email looks to be coming from a reliable source increases the likelihood that the receiver would open it and fall for the trick.
Legal Domains
In this kind of email spoofing attack, the attacker sends spoof emails using a genuine domain name, making it challenging for spam filters to recognize them as spam emails. Subsequently, the attacker could gain access to the recipient’s email account.
Lookalike Domains
In this kind of email spoofing attack, the scammer generates a domain name that accurately reflects a legitimate domain name by rearranging the domain names with closely spaced characters, causing recipients to believe that the email is from a reliable and trusted entity and making recipient to fall for the scam.
Nothing to worry about when many tools are available to save the day! As businesses and individuals have noticed the hype of email spoofing and the drawbacks of SMTP, they have started adopting tools to avoid email spoofing.
Reasons for Email Spoofing
There are many reasons that makes email spoofing possible. Following are the some of the reasons for email spoofing:
Phishing
According to AGG, 3.4 billion spam emails are sent every day, and the large majority of them are spam, with many of them being used in phishing emails. The majority of email spoofing attempts, known as phishing, involve appearing as trusted entities such as banks or state officials in order to fool recipients into disclosing their personal information. Also, attackers could employ strategies like attractive subject lines or images to get readers to click on the email, and they would ultimately achieve their intentions.
To be Ignored by Spam Filters
Hackers frequently use spoofed email addresses, which helps them escape spam filters because spoofed emails are less likely to be detected by spam filters and appear to be conventional emails.
Stealing the Information
Most spoof emails are sent with the intention of stealing private information, and because they look like regular emails, people fall for fraud and disclose their personal information.
You might be confused at this point between Phishing and Spoof emails. Don’t worry, we’ve got you covered!
Spoofing vs Phishing Emails
A spoof email can be used to initiate a phishing attack, giving the attacker the opportunity to create the email seem more believable and appealing. In simple words, claiming to be from a legit and authentic identity.
Phishing, on the other hand, is one of the social engineering methods in which an attacker sends a spoof email to a recipient using a spoof email address in an attempt to get their personal data.
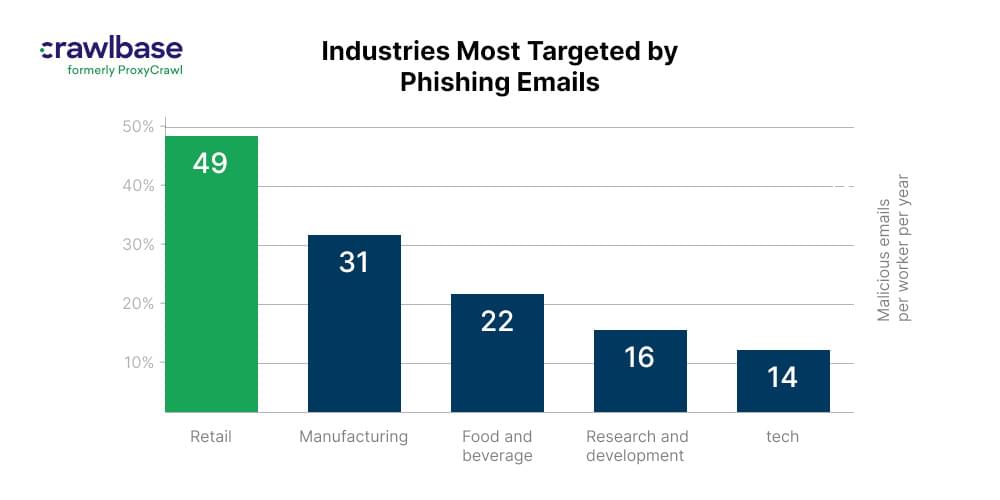
The Risks of Email Spoofing
According to Tessian, when it comes to industries receiving many scam emails almost all top dominating industries are affected. The reasons for email spoofing are relatively straightforward, but the potential risks associated with it are significant such as:
- Malware spread: The spoofing emails contain dangerous links or attachments, and if the receivers click on them, they unintentionally download viruses or are directed to websites that are infected with viruses and can damage their devices too.
- Damage to reputation: There is no doubt that if a spoof email is using a legit domain name that belongs to a reputed company, it will ultimately damage the reputation of the company, or it may destroy it.
- Financial Scam: Email spoofing is frequently used in financial scams and frauds, in which an attacker presents a legitimate identity while actually having criminal intentions.
These risks are so critical that, according to FBI, the total loss linked with spoofed emails was estimated at $2.4 billion in 2021 and recorded as the largest loss of all the time in 2014.
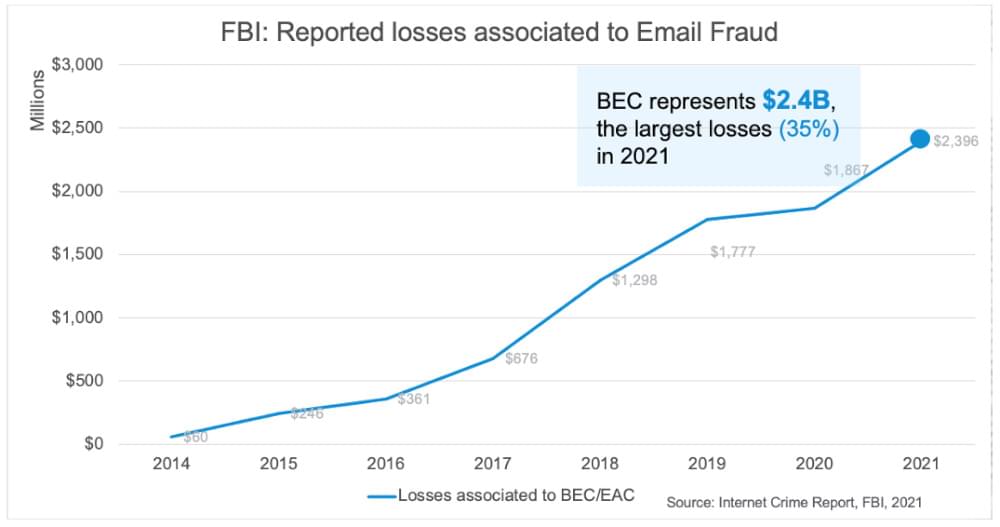
Moreover, the Internet Crime Report (IC3) received 19,954 complaints about BEC schemes in 2021 and almost estimated a total loss of $2.4 billion. By 2022, IC3 had received 21,832 attacks that were directed against both companies and Individuals, which resulted in a total financial loss of approximately $2.7 billion, a 3% rise from 2021.
According to CNBC report, in 2022 there were approximately 61% of people fell for phishing scams and put their data at risk. However, this is not going to end here!
Email spoofing scams are becoming more sophisticated and frequent than ever.
How to Detect Email Spoofing
Identifying email spoofing can be difficult, however, the following tips can help you spot possible spoofing. The email is most probably an email spoofing if:
- The email address doesn’t match the sender’s name.
- The reply-to address doesn’t match the sender’s address or the domain.
- The sender’s name and email address are not included in the organization’s employee directory, yet they claim to be from that organization.
- The name and domain of the firm or person who appears to be sending the email do not match the sender’s email address.
- If the email has typos, unusual language, grammatical errors, or unprofessional vocabulary, it may be an effort at email spoofing.
- The email employs the usual approach of urgency to force recipients to act without thinking ahead of time.
- Emails asking for some personal information such as credit card details.
Yet, there is good news: in 2021, the average percentage of spoof emails clicked/opened by the people was 17.8%, indicating that people are becoming smarter. Most people, according to Statistica, do not click on spoofed emails.
How to Protect Yourself From Email Spoofing
In most of the cases, you cannot avoid email spoofing, but you can protect yourself from the loss. To avoid falling into the trap of scammers, you need to be one step ahead of them! The following are some techniques that you can use to protect yourself from email spoofing.
- Email authentication is a mechanism that checks the sender’s domain and makes sure the email hasn’t been tampered with in order to avoid email spoofing. The three most popular email authentication mechanisms are.
- The Sender Policy Framework (SPF) makes a DNS record public to confirm that the sending mail server is authorized to send emails for a specific domain.
- DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM) encrypts emails in order to establish that they were sent from a legitimate domain and were not altered in transit, and use a digital signature.
- The Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance (DMARC) protocol allows domain owners to specify which mail servers are authorized to send emails in their name, enabling them to confirm the authenticity of emails sent from their domain.
- Email filtering is said to be a useful solution for identifying and blocking spam and spoof emails because it not only blocks emails but also attachments or links that come with them.
- Secure Email Gateways to scan all incoming and outgoing emails to prevent emails that do not conform to security regulations.
- Even if scammers have been able to spoof email, use multi-factor authentication to prevent them from causing further damages.
- Antivirus software to detect and block spoofed emails from reaching receivers’ mailboxes. (Important advice: Consistently update your antivirus software.)
However, If you think your email has been spoofed, It’s essential that you keep calm. Take a moment to collect yourself and properly assess the situation. As we previously discussed, there are several indicators that you may look for to identify a spoofing email. However, it is important not to act immediately in response to a suspected spoofed email, especially if it demands personal information or money transfers. Instead, spend some time thoroughly confirming the email’s validity and think about getting in touch with the sender personally or calling your email provider for advice.
Moreover, if your workplace email is spoofed, contact your IT manager as earliest as possible and spread awareness among other team members and colleagues about the spoofed address trying to scam you.
The good news is that no matter what kind of email spoofing incident you were the victim of, you can always report it to the authorities:
You should immediately notify law enforcement if the spoof email was a part of a phishing attack and intended to obtain your private or financial information. Furthermore, If the spoof email claims to be from a government agency or another reputed company, you should report it to both that company and the Federal Trade Commission (FTC).
Wrap up
Email spoofing is a common problem that usually goes unrecognized and affects both people and businesses in terms of financial loss due to lack of awareness. Hence, in order to be safe online, it’s important to protect yourself from email spoofing. This article attempted to provide thorough guidance on identifying email spoofing and strategies to prevent it, eventually minimizing the chances of online scams.
Stay alert and stay safe !
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How to spoof an email address with Gmail?
Email is vulnerable to email spoofing attacks because it relies on SMTP to send emails but does not offer enough mechanisms for sender authentication. To spoof an email address with Gmail, scammers may use this vulnerability to carry out email spoofing by forging email headers or by using a third-party email provider that allows email spoofing.
How do I stop spoofing emails from my email address?
If you think that your email address is being used for spoofing emails, the first thing you need to do is to change your credentials, enable multifactor authentication at your email, and use email authentication protocols such as SPF, DKIM, and DMARC.
How do hackers spoof your email address?
To spoof an email address, hackers use the following ways:
- Forging the email headers
- Modify email message components
- Use third-party email service that supports email spoofing.
- Use phishing attacks to steal your login credentials and gain access to your email account.
These ways allow hackers to spoof your email address.
What’s the difference between a hacked and a spoofed account?
In simple terms, a hacked account is when someone gains unauthorized access to your account by performing malicious behaviors. While spoofed accounts are impersonated or forged to appear to be coming from reliable sources (reliable domains and servers), yet, they are actually from spoofed addresses from different servers.