If you’re overwhelmed with manual price data extraction and want to learn how to scrape prices from Amazon using AI, then you’re in the right place. As you read through this blog, we’ll focus on automated scraping techniques, especially those involving automated XPath retrieval. We’ll walk you through setting up your scraping setup, using AI to get precisely the data you need, and mastering the art of automated data retrieval with XPath. Whether you’re a small online store or a big e-commerce giant, these techniques will be your superpowers in the digital world.
Crawlbase’s Crawling API enables you to scrape Amazon prices in combination with your preferred AI tool. You can sign up to use our ready-to-use Amazon Scraper; Your first 1000 requests are free of charge.
Crawlbase’s Crawling API enables you to scrape Amazon prices in combination with your preferred AI tool. You can sign up to use our ready-to-use Amazon Scraper; Your first 1000 requests are free of charge.
Table Of Contents
- Crawlbase Crawling API
- OpenAI GPT API
- Installing Python and Essential Libraries
- Creating a Virtual Environment
- Acquiring Tokens for Crawlbase and OpenAI
- Retrieving Amazon Search Page HTML
- Using OpenAI to Extract Price XPath
- Scraping the Amazon Product Prices
Importance of Automated Amazon Scraping
In order to perform scraping, you need to know the CSS selector or the XPath selector for the elements. Therefore, if you are scraping thousands of websites, you need to manually figure out the selector for each of them. And if the page changes, you need to change that as well. This is where automated web scraping Amazon comes into play, offering a pivotal advantage to those who harness its capabilities effectively.
Identifying the Data You Need for Scraping Amazon Prices
Amazon’s search pages are rich in data, but not all may be relevant to your specific scraping goals. Identifying the precise data elements you require is essential for efficient and focused scraping:
- Product Information: Determine which product details are vital for your objectives. This may include product titles, prices, customer ratings, and descriptions. Identifying these elements helps you extract the right information.
- Product URLs: If you intend to delve deeper into specific products, capturing the URLs to individual product pages is crucial. This allows you to access more detailed information for each item.
- Pagination Control: Understanding how pagination is structured on Amazon’s search pages is vital to collecting data from multiple result pages. You’ll need to locate and utilize the appropriate elements to navigate the pages efficiently.
As we progress through this blog, we’ll apply this knowledge to our automated scraping techniques. You’ll learn how to locate and extract the data you need from Amazon’s search pages, enabling you to gather valuable insights and make data-driven decisions in the world of e-commerce.
How to Scrape Amazon Prices: Step-by-step
Before embarking on your automated scraping journey, you must ensure you have the right tools and setup. This section will cover the initial preparation steps, including installing Python, creating a virtual environment, and acquiring the necessary tokens for Crawlbase and OpenAI.
1. Install Python and Essential Libraries
Python is the cornerstone of web scraping projects, and several libraries will play a pivotal role in your journey. Let’s start by ensuring you have Python and the following libraries installed:
Python Installation: If you don’t have Python installed, download the latest version from the official Python website and follow the installation instructions for your operating system.
Required Libraries: The following libraries are required to follow this blog successfully.
- Crawlbase Python Library: To interact with the Crawlbase Crawling API, you’ll need the Crawlbase Python library. This library simplifies the process of making requests to Crawlbase for web scraping. Install it with:
1 | pip install crawlbase |
- OpenAI Python Library: As you’ll be utilizing OpenAI’s GPT to get XPath, you need to install the OpenAI Python library. This library allows you to interact with OpenAI’s APIs effectively. Install it using:
1 | pip install openai |
- lxml: The Python lxml library is a robust and efficient tool for parsing and working with XML and HTML documents. It provides a powerful and user-friendly interface for navigating and manipulating structured data.
1 | pip install lxml |
2. Create a Virtual Environment
Creating a virtual environment is a best practice in Python development. It ensures that your project has its isolated environment with the required packages. Here’s how to set up a virtual environment:
- Install Virtualenv: If you don’t have virtualenv installed, you can do so using pip:
1 | pip install virtualenv |
- Create a Virtual Environment: Navigate to your project directory and run the following command to create a virtual environment:
1 | virtualenv venv |
- Activate the Virtual Environment: Depending on your operating system, the activation command may differ:
- On Windows:
1 | venv\Scripts\activate |
- On macOS and Linux:
1 | source venv/bin/activate |
Your virtual environment is now set up and activated. You can install project-specific packages without interfering with your system-wide Python installation.
3. Acquire Tokens for Crawlbase and OpenAI
To use the Crawlbase Crawling API and OpenAI GPT API, you’ll need to obtain the necessary tokens or API keys. Here’s how to acquire them:
Crawlbase Token: Visit the Crawlbase website and sign up for an account. Once registered, you’ll find your API token or key in the documentation. Crawlbase provides two types of tokens: the Normal Token (TCP) for static websites and the JavaScript Token (JS) for dynamic or JavaScript-driven websites. For Amazon, we need a JS token. Keep this token safe, as it will be essential for accessing the Crawlbase API. For an easy start, Crawlbase gives 1000 free requests for its Crawling API.
OpenAI GPT Token: Visit the OpenAI website and create an account if you haven’t already. Access your API token from your OpenAI account settings. This token is required for making requests to the OpenAI GPT API.
In the following sections of this blog, we will guide you through the practical steps of scraping product prices from Amazon’s search pages efficiently and effectively. Stay with us as we explore the tools and techniques that will give you a competitive edge in e-commerce.
Automating Amazon Price Scraping
Now that you’re well-prepared and equipped with the necessary tools and tokens, it’s time to dive into the heart of automated scraping. This section will guide you through the detailed steps of scraping Amazon product prices using the Crawlbase Crawling API and OpenAI.
Retrieving Amazon Search Page HTML
The first step in automating price scraping is to obtain the HTML content of Amazon’s search pages. This HTML content is where the product information, including prices, is embedded. Just like many modern websites, Amazon’s search pages use fancy technology like JavaScript and Ajax to load their content. This can make it tricky to scrape data from these pages. But, with the Crawlbase Crawling API, you have the tools to handle these challenges effectively. Below is the Python script to retrieve HTML of Amazon search page for query macbook .
1 | from crawlbase import CrawlingAPI |
When using the JavaScript token with the Crawlbase API, you can specify some special parameters to ensure that you capture the dynamically rendered content accurately. You can read about them here.
- page_wait: This optional parameter allows you to specify the number of milliseconds to wait before the browser captures the resulting HTML code. Use this parameter in situations where a page takes time to render or when AJAX requests need to be loaded before capturing the HTML.
- ajax_wait: Another optional parameter for the JavaScript token. It lets you specify whether to wait for AJAX requests to finish before receiving the HTML response. This is important when the content relies on AJAX requests.
output.html Preview:
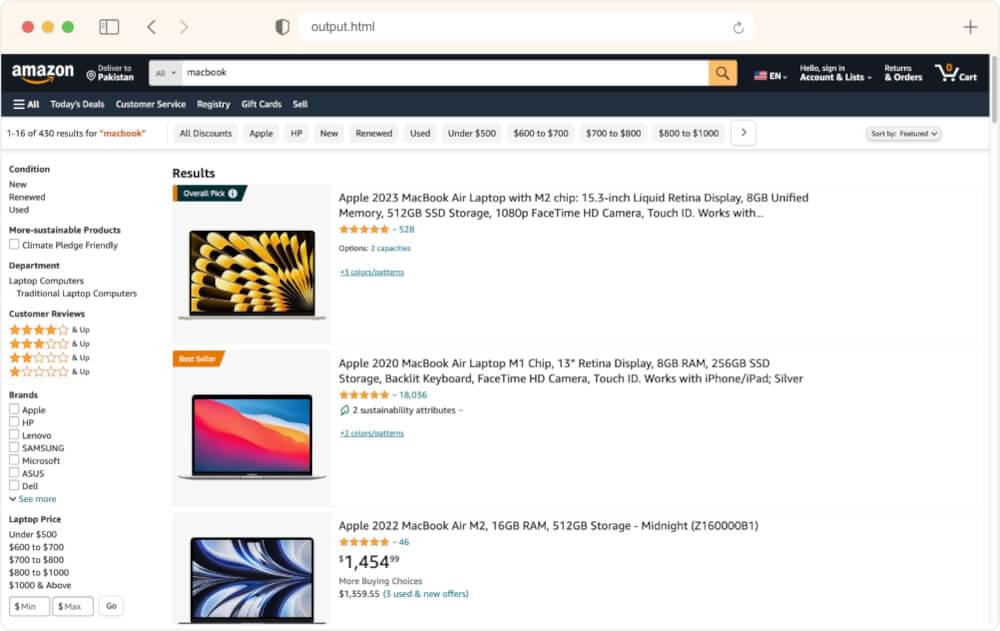
Using OpenAI to Extract Price XPath
In our quest to automate the extraction of product prices from Amazon’s search pages, we turn to the remarkable capabilities of OpenAI, specifically the GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer) model. Lets update the previous example and add the code to utilize OpenAI to generate precise XPath expressions for extracting product prices from HTML content effectively utilizing GPT-4 prompts for optimal accuracy:
1 | import openai |
This code is the bridge between your HTML content and the precise XPath expressions needed to locate and extract product prices. It initiates communication with OpenAI’s GPT-3.5 Turbo engine, provides instructions, and receives generated XPath expressions tailored for your scraping needs. The generated XPath is then readily available for your web scraping tasks, streamlining the process and enhancing precision.
4. Scraping the Amazon Product Prices
To take your scraping journey to the next level, we’ll enhance the previous example script by adding a function called find_max_price. This function utilizes the Python lxml library to parse the HTML content and select all product prices based on the generated XPath expression. It then converts the selected price strings to numerical values and identifies the highest price using the max() function. Finally, the script prints the highest Macbook price found on the Amazon search page, providing you with a valuable data point.
1 | import openai |
Example Output:
1 | The highest macbook price is: 5,299 |
With this addition, your scraping script now not only retrieves data but also processes it to provide you with valuable insights, such as the highest Macbook price found on the Amazon search page. You may also want to know how to handle pagination while scraping and saving the results in a proper format. For this, you can refer to this blog. Enjoy your enhanced scraping capabilities!
Final Thoughts
We hope this blog helps you automate your scraping efforts and saves you alot of time. If you’re interested in scraping Walmart product data or its search pages, consider exploring the following guides:
📜 How to Scrape Amazon Reviews
📜 How to Scrape Amazon Search Pages
📜 How to Scrape Amazon Product Data
You can find additional guides like scraping amazon ASIN, Amazon reviews in Node, Amazon Images, and Amazon data in Ruby. Additionally, for e-commerce scraping guides beyond Walmart, check out our tutorials on scraping product data from Walmart, eBay, and AliExpress.
Feel free to reach out to us here if you need further assistance or have additional questions.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What should I do with the scraped Amazon price data?
What you do with the scraped price data from Amazon largely depends on your intentions and compliance with relevant legal regulations. If you plan to use the data for personal use or analysis, you may typically do so as long as it aligns with Amazon’s terms and conditions and the applicable web scraping laws in your region. However, sharing, selling, or publishing scraped data, especially for commercial purposes, often requires explicit permission from Amazon.
Q: How can automated scraping Amazon benefit my e-commerce business?
Automated scraping offers several advantages for e-commerce businesses. It allows you to monitor competitive price scraping and product offerings continuously. It provides in-depth insights into product trends, customer preferences, and market demands, which are invaluable for product development and targeted marketing. Additionally, accurate and up-to-date product information on your e-commerce website ensures a seamless shopping experience for customers.
Q: Can I adapt automated scraping Amazon to handle changes in website layouts?
Yes, automated scraping can adapt to changes in Amazon website layouts. When websites update their design or structure, automated scraping can use techniques such as CSS selectors and flexible XPath expressions to ensure that data collection remains uninterrupted. This adaptability is valuable, allowing you to maintain accurate and up-to-date data even when websites change their appearance.
Q: What is an Amazon price scraper?
An Amazon price scraper is a tool or script that automatically extracts product prices from Amazon. It mimics how humans use Amazon, collecting real-time price information for products, including discounts, original prices, and price changes over time.