You have likely asked this question more than once. The thing is that most people get curious about many things, especially those things they interact with on a regular basis, of which Google (search) is part of most of us.
Most people intrigued by the way Google can get them the result of what they search in a matter of seconds would likely have asked the question, ‘How Does Google Search Work?’ instead of ‘How Does Google Scrape Websites?’ they both relate since answering one would lead you to talk about the other.
So we will be talking about google website scraping, how Google scrapes websites for information, how Google search works, why you need Google website data extraction, and Google’s web scraping techniques.
Google Website Scraping
Google website scraping refers to extracting data from Google’s website using automated tools or software. There are several ways to scrape Google website data, including search results from Google’s search engine, scraping Google Maps data, and various other ways.
How Google Search Works
The Google Search engine looks through hundreds of billions of web pages and other content stored in our Search index to find information for you, which is more than all of the world’s libraries from all over the world combined.
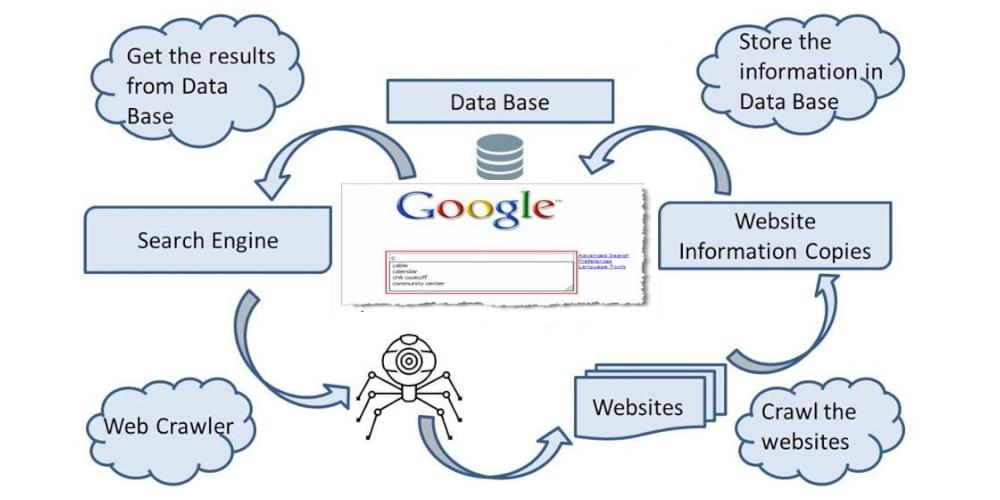
Here’s exactly all you need to know on the number one most visited and used website on the internet works. Google search works in these three steps:
- Crawling
With the help of automated programming, known as crawling, Google constantly downloads texts, images, and videos from web pages it finds on the internet.
- Indexing
While analyzing a web page, Google analyzes the page’s text, images, and video files and stores the information in its index, a pervasive collection of information.
- Serving
Google’s policy is to return information relevant to a user’s search query when they search on the search engine.
It isn’t as simple as it seems, but the above is just the summary of how Google works inside one of these lies scraping. Yes, Google scrapes data from other websites too, but before we go into that, let’s explain what happens before any website appearing on the Google SERP (Search engine Result Page) shows up on your result.
SERP means extracting data from different engines (Google, Bing, Yahoo, etc.) Search Engine Result Pages. These pages contain heaps of valuable data, which you can use to create marketing strategies, optimize SEO, monitor competitors, create e-commerce projects, and more. To improve your rankings and online visibility, investing in off-page SEO services can help build authority through backlinks, social signals, and other external factors.
The webmaster publishes their website they notify Google saying ‘hey! I just published my site, and I want you to show it to searchers when they search (any term could fit in here) keyword’ they do this by submitting their site to the Google webmaster tools and allowing the Googlebot (Google’s web crawler) access to their website pages through the robots.txt file.
Google responds by sending its crawler to go through the site and confirm if it exists, what pages are available, and gets the kind of content available on it. If the site meets Google’s requirements, they start showing up on the SERP.
Why Do You Need Google Website Scraping?
Several search engines are available on the market, but Google reigns supreme. The world cannot discover your business if it doesn’t appear on page one of Google search results. When we compare different search engines, it is clear that Google is the most used search engine with the highest market share because we see businesses live and die by Google’s ranking results.

Undoubtedly, Google dominates the search engine market, but knowing how many searches are being done in different countries and on different devices can be helpful - especially if you want to rank for specific countries or devices.
There are several reasons why businesses scrape Google for their needs. However, the most common reasons are as follows:
- Identifying competitors and market prices
- Keeping track of search engine optimization (SEO)
- Searching for specific keywords to build URL lists
- Analyzing keyword rankings
- Analyzing paid and organic traffic
- Advertising analysis
Google, however, does not appear to offer a simple way to extract data from its search engine results pages - at least as of yet. For this reason, scraping is necessary for downloading results.
Google’s Data Scraping Methods
There are various methods by which Google extracts information from websites to pull data from them:
- Web Crawling
A web crawler or spider is a program that automates internet browsing to gather information and follow links from one page to another.
- Parsing HTML
Web crawlers perform a process of parsing HTML code for web pages to extract information from them, such as text content, images, links, and metadata, as soon as they encounter a new web page.
- Indexing
Google’s index, an enormous database of web pages and their associated information, is the repository for the extracted data.
- Ranking
Ranking web pages in Google’s search results depends on various factors. It depends on several factors, including the content’s relevance and quality, the website’s authority, trustworthiness, and the user’s search history and location.
- Monitoring and Updates
Google continuously crawls and updates its index for accurate and up-to-date search results. Additionally, webmasters can monitor how their websites perform in Google’s search results using various tools and services from the site.
It is essential to keep in mind that Google’s data extraction method is to provide a valuable service to users searching for information online while respecting the rights of the owners of the websites as well as adhering to ethical and legal norms.
How Does Google Scrape Websites?
For Google to index your site, it needs to crawl and then scrape the contents of your website. This means that Google crawls your site using Googlebot (Google’s web crawler) and scrapes your website content, storing it in a cached form.
Why does Google need to store and cache your website on its servers when your site is online? This is for faster delivery of search results to searchers serving results from Google’s servers obviously would be faster than from your host or any other third-party server.
So exactly how does Google extract data from websites? The first step to Google scraping any website is by first sending Googlebot to crawl the website and all of its pages and related links by so doing, Google has an idea of what kind of data is available on the website, and the next is scraping the content of the website. Now, Google uses its in-house web scraper to fetch data from the website.
For Google to deliver accurate and relevant search results, it considers many factors, including the quality and relevance of the content, the authority and trustworthiness of the website, and the location and search history of the user.
In a nutshell, a webmaster first notifies Google of their website and its address. Google sends Googlebot to confirm what pages exist and are available on the website, then scraping starts, after which the site index and ready to serve on the SERP to searchers.
Considerations Before Searching on Google
You can use Google’s search function to find the answer to any question in today’s world. Millions of people have used the search engine to find answers to their strange or complicated questions.
Most people look for faster search results and optimum results when they search for something on Google. If you are looking for faster results using Google, you can review our tips for Google search.
Here are the basic things you should consider to get better Google search results.
- Try to Keep It Simple
Make your search as simple and web-friendly as possible. Adding relevant or essential words is an effective way to improve the search result. Start by entering one or two words and gradually increasing their number if you aren’t satisfied.
In search engines, less is more if you search for fewer words, the search engine will provide more results.
- An Order of Priority for Keywords
Make your search more effective by choosing the right keywords. When you choose keywords wisely, search results will be more efficient if they aren’t, results will be less efficient.
Think about the words the author would use to describe what you’re looking for, and write/describe them in your own words. Ensure you order your words accurately while searching for a phrase or quote.
- Cut out Unnecessary Information
You can ignore most of your typos and other things that Google can handle. Therefore, you should skip these things from your query.
Write a search query without worrying about the following:
Spelling
Punctuation (dot, question mark, exclamation mark, etc.)
Cases (uppercase or lowercase)
Special characters (plus, minus, brackets, and more)
Searching on Social Networks
The search engine Google does an excellent job when it comes to searching for people and social networks. You can search for people and their social profiles by:
#<word>- direct username
The simplest way to find hashtags on Twitter, Facebook, and other social networks is by adding a ‘#’ before any word in the search engine.
How to Use Data Extracted from Google?
There are billions of people around the world who rely on Google as their first gateway to the internet. Due to this, almost all businesses consider appearing in Google search results to be a key factor in their marketing strategy. Local businesses’ online profiles significantly impact the reputation and reviews they receive on Google.
Acquiring reliable SEO tools is particularly important for marketing agencies with numerous industry clients. Using such systems is a way to efficiently perform multiple tasks and a means of monitoring and analyzing the system’s performance for successful management.
- If you want to dig deeper, you can take it further and analyze the links between your site and the top-ranking pages.
- Google Search scraping is typically used for the following purposes, among many others.
- Determine the main trends of Google’s algorithm by analyzing it.
- Track how your website performs over time for specific queries in Google to gain insights for Search engine optimization (SEO).
- Identify the keywords that are most likely to be relevant to a given set of ads.
- Keep an eye on both organic and paid results for the competition.
- Identify specific keywords and build a URL list. You can use this if you scrape web pages containing specific phrases and need relevant starting points.
Google’s Web Scraping Techniques
The Google search engine is arguably the most ubiquitous tool on the internet it accounts for 92.9 % of all web searches. Thanks to the proliferation of smartphones, anyone can search for anything from wherever they are – just as long as they have an internet connection. As a result, Google serves several billion searches a day, which is quite a substantial number.
You probably need to learn more about Google, even if you use it several times daily. Here are some tips for improving your Google skills if you need help to get the desired results.
- Make Your Searches More Specific with Operators
Even when you need more clarification, Google’s search algorithm returns the information you seek. If Google does not provide what you need in search results, you can refine them with operators. Following are the search operators you can use:
To find the exact phrase, use quotation marks (“ “)
Add a tilde (~) in front of a word to find synonyms
Delete terms with a minus sign (-)
To search for a range of numbers, insert two periods (..) between the numbers
Add a site: to search one particular website
Browse file types
Explore the Advanced Search Options
Not interested in learning all these modifiers? Google’s advanced search allows you to use them. You can open the advanced search page by clicking the gear icon on the Google results page.
Instead of relying on specific modifiers, you can enter keywords or phrases in specific fields. The results can narrow down even further depending on the language, region, last update, domain, term location, explicit content, file type, and usage right. Narrowing down image searches by size, aspect ratio, color, and type is also possible.
Mobile users can filter their image search but not create an advanced one. Using the slider icon at the top of your search page, you can filter images based on the most recent GIFs, HD images, product images, and usage rights.
- Identify Time Constraints
Do you want to find the latest information about a subject or information relevant to a specific period? To filter your search results, use Google’s desktop and mobile tools. Under the magnifying glass icon on the desktop, click Tools. You can select Search tools on mobile by swiping toward the end of the list of Google search types.
You can narrow your search results by selecting Any time to see results from the past hour, 24 hours, week, month, or year. Users can enter specific dates using the Custom range option on the desktop.
- Quotes from Real-Time Stocks
The Google Graph will display real-time price information about publicly traded companies, labeled with a ticker symbol. For example, Type in GOOG for Alphabet, AAPL for Apple, or AMZN for Amazon, and Google will display real-time price information about those companies.
- Filter Out Explicit Content
Does your child use the computer? Use Google’s SafeSearch feature to keep them away from explicit content. Toggle on the Explicit results filter on the search results page by clicking the gear icon on the top right. Even though Google admits the filter isn’t 100% accurate, it filters out explicit links, images, or videos appropriate for all audiences. Visit our Best Parental Control Software picks for a more robust solution.
Well done! Now you know all the valuable search techniques for making better searches on the internet and all the tips and tricks you can use to get more reliable and accurate results. Using this tool will save you time and resources.
Can You Scrape the Search Results from Google Without Getting Blocked?
Proxy servers mask your scraper’s IP address, help avoid Google’s anti-bot system (e.g., reCAPTCHA), and make geotargeting much easier (e.g., UULE). A proxy will make your scraper much easier to detect with one. The chances of your successful request will be significantly reduced because you won’t be able to send most requests. You may also want to pay attention to the user agent.
Which Browser is Best for Scraping Google Search Results?
Usually, developers use headless browsers instead of regular browsers, which offer better automation features and lack a graphical interface. There is no doubt that Headless Chromium may be the most popular headless browser on the market since Chromium is the world’s most popular web browser platform. Other options, such as Headless Firefox, PhantomJS, and HTMLUnit.
Final Remarks
In this post, we covered a lot of details about how Google scrapes websites and how Google searches work, and we hope that the above information will be valuable to you.
You are at the right place if you are looking for a simple and reliable way to create your Googlebot, look at Crawlbase.