Scraping, analyzing, and storing data doesn’t have to be complicated. If you pair Crawlbase with GoogleSQL using BigQuery, connecting web data straight into your analytics becomes much easier. In this guide, we’ll show you a step-by-step guide on how to set up Crawlbase, grab the data you need, and load it all into Google Cloud SQL, so you can start asking smarter questions and getting clear answers with ease.
What is GoogleSQL?
GoogleSQL is a part of Google Cloud’s managed SQL database services, like Cloud SQL or BigQuery. Imagine you need somewhere safe in the cloud for your data, Google Cloud SQL is basically a home for databases like MySQL, PostgreSQL, and SQL Server, all managed by Google so you don’t have to worry about the hardware or most of the complicated setup. You pop your data in, and Google handles most of the work on the backend.
If you hear someone mention GoogleSQL, it’s often about the SQL language flavor that BigQuery uses for slicing big data. So, in plain terms, “Google SQL” usually means using Google’s cloud-based tools for storing data and running SQL queries, without needing to manage your own servers or install anything complicated. You can simply connect, write queries, and let Google do the rest.
Steps to use GoogleSQL in Crawlbase
Here are the following steps to use Google SQL in the Crawlbase environment:
Step 1: Set Up Crawlbase and Python Environment
Now that your environment is ready, let’s fetch some real data to work with. First thing to do is to secure your Crawlbase account. So go ahead and follow the steps below if you don’t have an account yet.
- Create an account at Crawlbase and log in.
- After registration, you will receive 1,000 free requests. To get an extra 9,000 requests for free, simply add your billing details before consuming any of the free trial credits.
- Locate and copy your Crawling API Normal requests token.
Next, we need to make sure the compatible Python version and the Requests library are properly installed. So, follow the steps below.
- Install Python 3 on your computer
- Create a root directory in our filesystem.
- Go to your terminal and run
pip install requests
Step 2: Crawl Data For Database Import
The next step is to collect the data you’ll import into your database. Below is a simple Python script that uses the Crawling API to scrape Amazon product data and save it as a CSV file. So, copy the script below and save it to crawl_data.py
1 | from requests.exceptions import RequestException |
To run the script, simply use the command below:
1 | python crawl_data.py |
This will generate a CSV file named data.csv, which we’ll use in the next section.
Step 3: Set up Google Cloud SQL Database
Before you can analyze your scraped data, you’ll first need to set up a Cloud SQL database in Google Cloud. Here’s how to create an instance, add a database, and set up a table where your scraped Amazon product data will go.
- Go to Google Cloud Console.
- Create a new project or select an existing one.
- You need to enable billing on your project to use Cloud SQL.
- Enable the Cloud SQL:
- Go to the Google Cloud Console
- Navigate to “API & Services” > “Dashboard”
- Click “Enable APIs & Services”
- Search for “Cloud SQL” and select it, and click “Enable”
- Create a Cloud SQL Instance:
- Go to the Cloud SQL Instances page in the Google Cloud console.
- Click “Create instance”.
- Choose a database engine (MySQL, PostgreSQL, or SQL Server), this time we “Choose PostgreSQL”.
- Configure the instance settings (Instance ID, Region, etc.).
- Set a password for the root user.
- Click “Create instance”.
- Create a database:
- Go to the Cloud SQL Instances page.
- Select the instance you want to configure.
- Navigate to the “Databases” tab.
- Create a database called “analytics_example_db”.
- Create a table:
- Go to the Cloud SQL Instances page.
- Select the instance you want to configure.
- Navigate to the “Cloud SQL Studio” tab.
- Log in to “analytics_example_db” database
- Click the [+] to create a new tab
- Paste the SQL scripts below and click Run
1 | CREATE TABLE "public"."amazon_products" ( |
This will create a new table called amazon_products
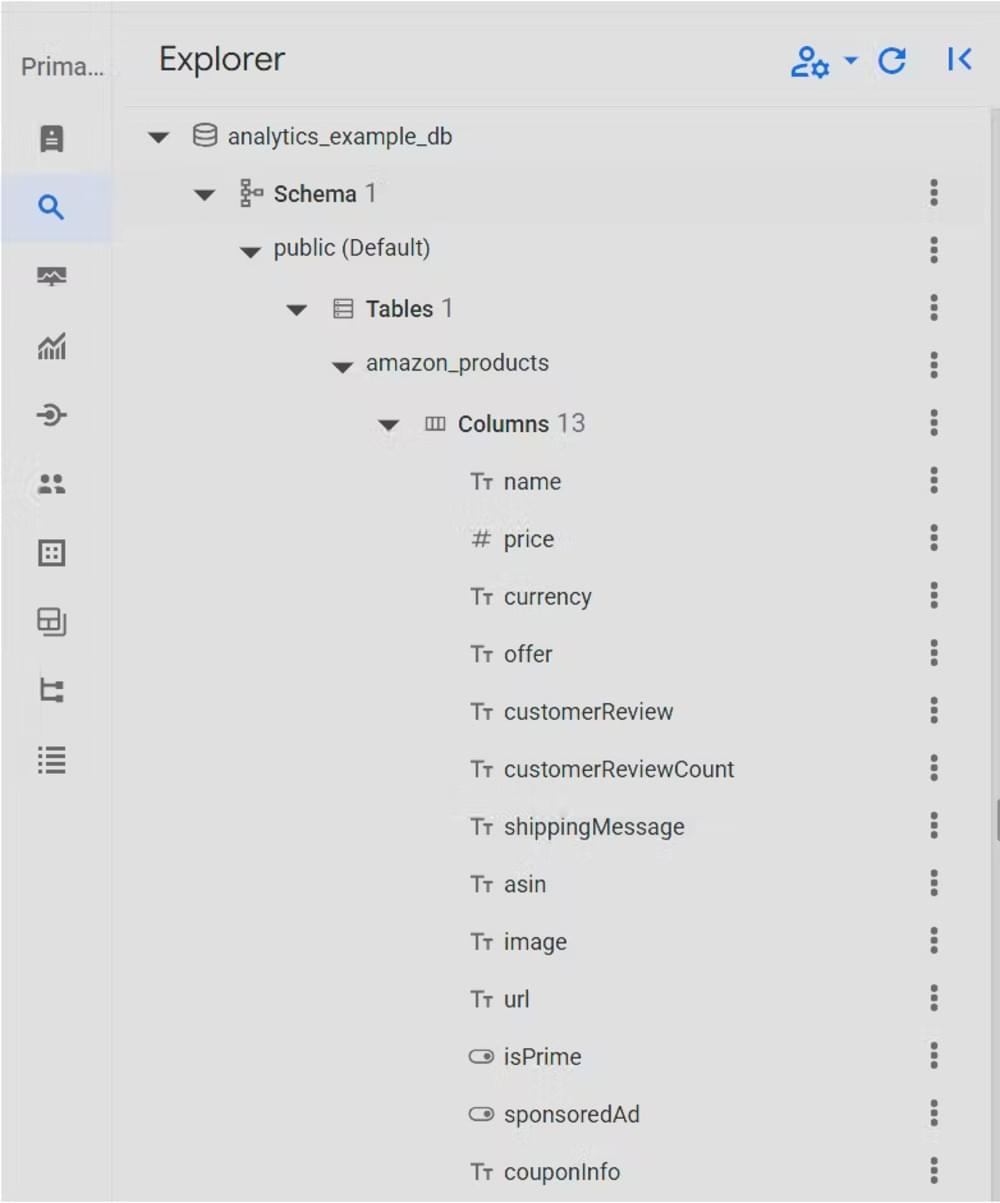
Step 4: Import Crawled Data Into Crawlbase Database
The final step is to import the scraped CSV file into your Cloud SQL database now that the table is ready. Follow these steps to upload the data and make it available for querying with Google SQL.
- Select a Cloud SQL Instance:
- Go to the Cloud SQL Instances page.
- Select the instance you want to configure.
- Go to Overview → Import
- Select CSV as a File Format
- Upload files from your computer as a source file
- Browse to the
data.csvcrawled from above. - Create a unique Cloud Storage location name.
- Upload the
data.csvto the bucket. - Select
analytics_example_dbas the Destination database - Set table name to
amazon_products - Click Import
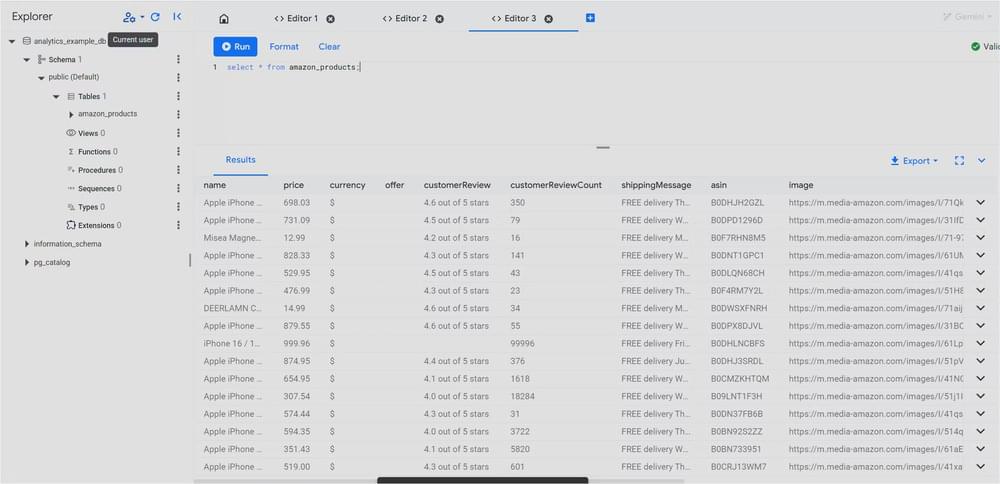
You’ve now successfully imported your scraped data into Cloud SQL. With everything in place, you can start running queries and exploring the data using Google SQL to gain valuable insights.
Give Crawlbase a try now and see what you can accomplish!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q. Do I need to pay to use Google Cloud SQL?
A. You need to enable billing to use Cloud SQL, but the good news is that Google offers free credits for new users. You can try it out without spending money right away.
Q. Can I use this method to import data from other websites, not just Amazon?
A. Yes, this setup is not limited to Amazon. You can scrape data from any public website using Crawlbase, then follow the same steps to store and analyze it in Google Cloud SQL.
Q. What happens if my data format changes later on?
A. No worries! If your scraped data changes (for example, new fields are added), you can easily update your Cloud SQL table. Just use an ALTER TABLE command to add new columns while keeping your existing data safe.