Scraping with Python is a popular method for automating data extraction from Amazon, allowing users to efficiently gather large volumes of product information. However, scraping Amazon’s search results at scale is a challenging feat, mainly due to the vast data, intricate web layouts, rate limitations, CAPTCHAs, and other security measures in play.
This comprehensive guide will explore how to scrape Amazon search pages at scale using Python and the Crawlbase Crawling API. In this tutorial, we will focus on scraping Amazon product data and demonstrate web scraping activity, including setting up the necessary tools and techniques. You can efficiently extract and analyze product data from Amazon by leveraging this powerful combination.
Our ready-to-use Amazon scraper is a comprehensive solution for extracting key data from Amazon. You can try it now.
Table of Contents
- Setting Up Your Development Environment
- Installing Required Libraries
- Creating a Crawlbase Account
- Dynamic Content and JavaScript Rendering
- Getting the Correct Crawlbase Token
- Setting up Crawlbase Crawling API
- Handling Dynamic Content
- Choosing a Scraper
- Handling Pagination
1. Why Scrape Amazon Search Pages?
In the vast world of online shopping, Amazon stands as a giant. It boasts an unparalleled selection of products across an extensive range of categories, making it a go-to destination for shoppers worldwide. Data gathering from Amazon is crucial for business intelligence, as it enables companies to analyze trends, monitor competitors, and make data-driven decisions.
Crawlbase Python Library
To harness the power of Crawlbase Crawling API, you can use the Crawlbase Python library. This library simplifies the integration of Crawlbase into your Python projects, making it accessible to Python developers of all levels of expertise.
First, initialize the Crawling API class.
1 | api = CrawlingAPI({ 'token': 'YOUR_CRAWLBASE_TOKEN' }) |
Pass the URL that you want to scrape by using the following function.
1 | api.get(url, options = {}) |
You can pass any options from the ones available in the API documentation.
Example:
1 | response = api.get('https://www.reddit.com/r/pics/comments/5bx4bx/thanks_obama/', { |
There are many other functionalities provided by Crawlbase Python library. You can read more about it here.
In the following sections, we will guide you through harnessing the capabilities of the Crawlbase Crawling API to scrape Amazon search pages effectively. We’ll use Python, a versatile programming language, to demonstrate the process step by step. Let’s explore Amazon’s wealth of information and learn how to unlock its potential.
2. Prerequisites
Before we embark on our web scraping journey, let’s ensure that you have all the necessary tools and resources ready. In this chapter, we’ll cover the prerequisites needed for successful web scraping of Amazon search pages using the Crawlbase Crawling API.
Setting Up Your Development Environment
You’ll need a suitable development environment to get started with web scraping. Here’s what you’ll require:
Python:
Python is a versatile programming language widely used in web scraping. Ensure that you have Python installed on your system. You can download the latest version of Python from the official website here.
Code Editor or IDE:
Choose a code editor or integrated development environment (IDE) for writing and running your Python code. Popular options include PyCharm, and Jupyter Notebook. You can also use Google Colab. Select the one that best suits your preferences and workflow.
Installing Required Libraries
Web scraping in Python is made more accessible using libraries that simplify tasks like making HTTP, parsing HTML, and handling data. Install the following libraries using pip, Python’s package manager:
1 | pip install pandas |
Pandas: Pandas is a powerful data manipulation library that will help you organize and analyze the scraped data efficiently.
Crawlbase: A lightweight, dependency free Python class that acts as wrapper for Crawlbase API.
Creating a Crawlbase Account
To access the Crawlbase Crawler API, you’ll need a Crawlbase account. If you don’t have one, follow these steps to create an account. Click here to create a new Crawlbase Account and fill the necessary details.
3. Understanding Amazon Search Page Structure
Before we embark on our web scraping journey, it’s essential to understand the structure of an Amazon search page. Amazon’s web pages are meticulously designed to provide a seamless shopping experience, but a wealth of valuable data lies beneath the user-friendly interface. Amazon provides the following URL for the search queries.
1 | # Replace serch_query with your desire one |
Identifying Data Points of Interest
To scrape Amazon search pages effectively, you need to identify the specific data points you want to extract. Depending on your objectives, you might be interested in various pieces of information, including:
- Product Title: The name of the product being sold.
- Price: The current price of the product.
- Seller Information: Details about the seller, such as their name and ratings.
- Product Availability: Information about whether the product is in stock or out of stock.
- Product URL: The URL that leads to the product’s page on Amazon.
- Customer Ratings: Ratings and reviews provided by customers who have purchased the product.
- Product Features: Key features or attributes of the product.
- Shipping Information: Details about shipping options, including delivery times and costs.
- Sponsored Listings: Amazon often includes sponsored listings at the top of search results. These are paid advertisements.
Like many modern websites, Amazon employs dynamic loading of content using JavaScript rendering and Ajax calls. This means some parts of the page, such as search results and filters, may not be present in the initial HTML source code. Instead, they are loaded dynamically after the page is initially loaded in the user’s browser.
4. How to Scrape Amazon Search Pages
In this section, we embark on an exciting journey to scrape Amazon search pages at scale using the Crawlbase Crawling API. For example, we will gather essential information about products related to the search query “games” on Amazon. To accomplish this, we’ll employ the Crawlbase Python library, which offers seamless integration with the Crawling API. Let’s dive into the process:
Getting the Correct Crawlbase Token
We must obtain an API token before we can unleash the power of the Crawlbase Crawling API. Crawlbase provides two types of tokens: the Normal Token (TCP) for static websites and the JavaScript Token (JS) for dynamic or JavaScript-driven websites. Given that Amazon relies heavily on JavaScript for dynamic content loading, we will opt for the JavaScript Token.
1 | from crawlbase import CrawlingAPI |
You can get your Crawlbase token here after creating account on it.
Setting up Crawlbase Crawling API
With our JavaScript token in hand, we are ready to configure the Crawlbase Crawling API. Before starting further, we need to know about the output response structure. You can receive the output response in two types: HTML or JSON. By default, Crawling API uses HTML format.
HTML response:
1 | Headers: |
To get the response in JSON format you have to pass a parameter “format” with the value “json”.
JSON Response:
1 | { |
We can read more about Crawling API response here. For the example, we will go with the default option. We’ll utilize the initialized API object to make requests. Specify the URL you intend to scrape using the api.get(url, options={}) function.
1 | from crawlbase import CrawlingAPI |
In the code snippet above, we are preserving the retrieved HTML content by saving it to an HTML file. This step is essential for verifying that we have successfully obtained the desired HTML data. We can preview the file and see which content is included in the crawled HTML.
output.html Preview:
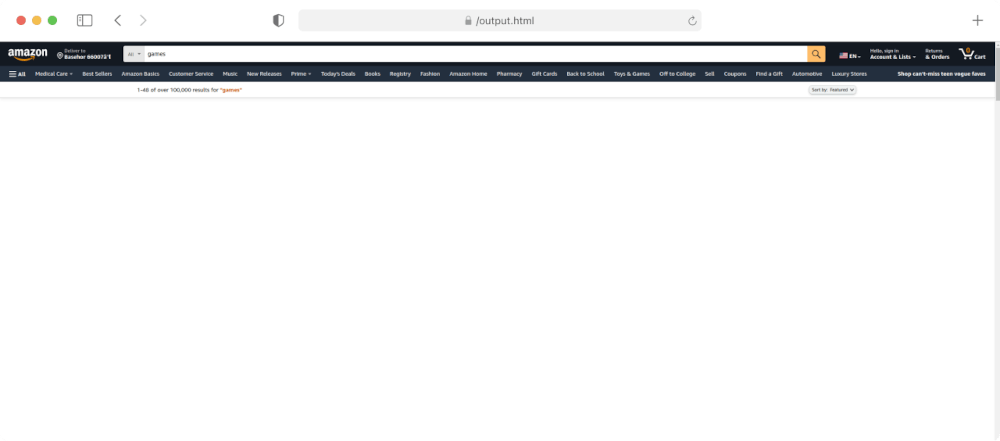
As you can see above, no useful information is present in the crawled HTML. This is because Amazon loads its important content dynamically using JavaScript and Ajax.
Handling Dynamic Content
Like many modern websites, Amazon search pages employ dynamic loading of content using JavaScript rendering and Ajax calls. This dynamic behavior can pose challenges when attempting to scrape data from these pages. However, with the Crawlbase Crawling API, you can effectively overcome these challenges. We can use the following query parameters provided by Crawling API to overcome this problem.
Adding Parameters
When using the JavaScript token with the Crawlbase API, you can specify some special parameters to ensure that you capture the dynamically rendered content accurately. Here are some crucial parameters:
- page_wait: This optional parameter allows you to specify the number of milliseconds to wait before the browser captures the resulting HTML code. Use this parameter in situations where a page takes time to render or when AJAX requests need to be loaded before capturing the HTML.
- ajax_wait: Another optional parameter for the JavaScript token. It lets you specify whether to wait for AJAX requests to finish before receiving the HTML response. This is important when the content relies on AJAX requests.
For using these parameters in our example, we can update our code like this:
1 | from crawlbase import CrawlingAPI |
output.html Preview:
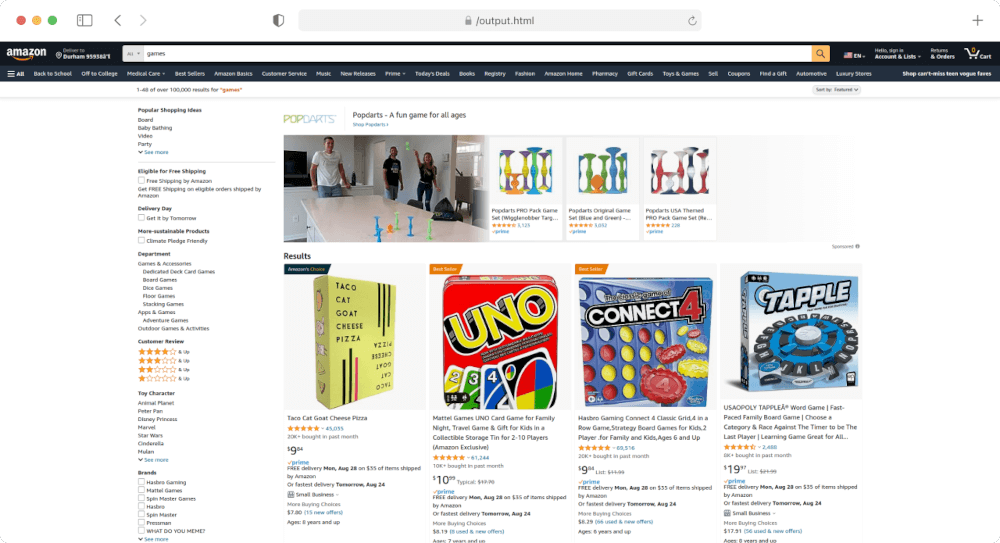
Crawling API provides many other important parameters. You can read about them here.
Choosing an Amazon Scraper
Crawling API provides multiple built-in scrapers for different important websites, including Amazon. You can read about the available scrapers here. The “scraper” parameter is used to parse the retrieved data according to a specific scraper provided by the Crawlbase API. It’s optional; if not specified, you will receive the full HTML of the page for manual scraping. If you use this parameter, the response will return as JSON containing the information parsed according to the specified scraper.
Example:
1 | # Example using a specific scraper |
One of the available scrapers is “amazon-serp”, designed for Amazon search result pages. It returns an array of products with details like name, price, customer reviews, and more. Here’s an example of the output from the “amazon-serp” scraper:
1 | { |
This includes all the information we want. Since the response will be JSON this time, we will store some important information of every product object into a CSV file. So, lets add this parameter into our example and do the changes as per the response:
1 | from crawlbase import CrawlingAPI |
In the above code, we added the scarper in the options and then collected all the information we wanted for each product JSON object inside the response. Last, we are creating a Pandas data-frame to use its “to_csv” function to save the data in a CSV file.
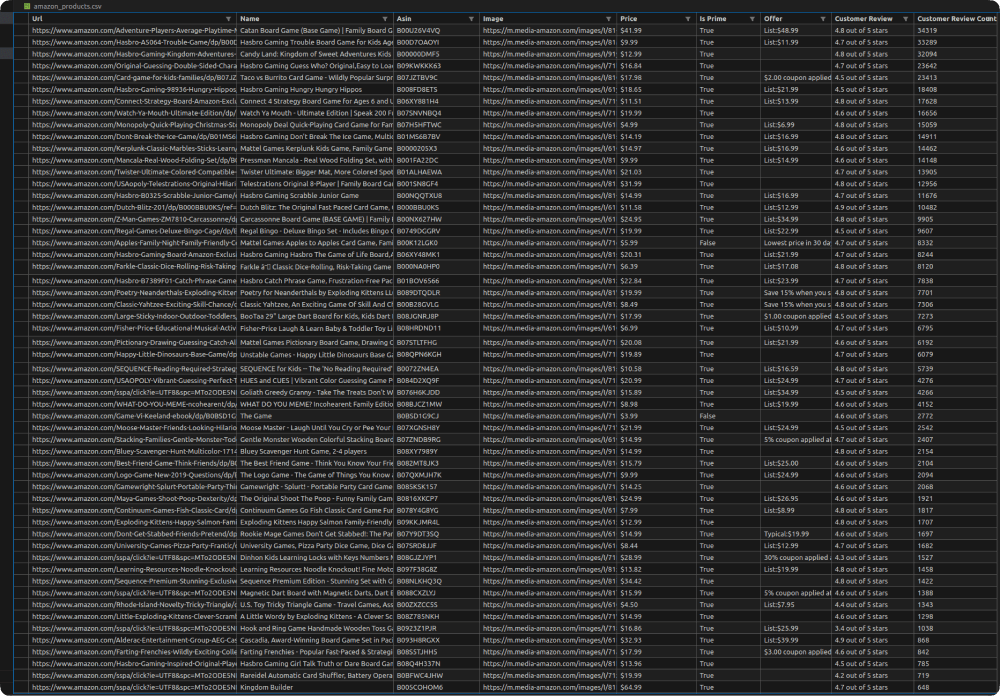
amazon_products.csv Preview:
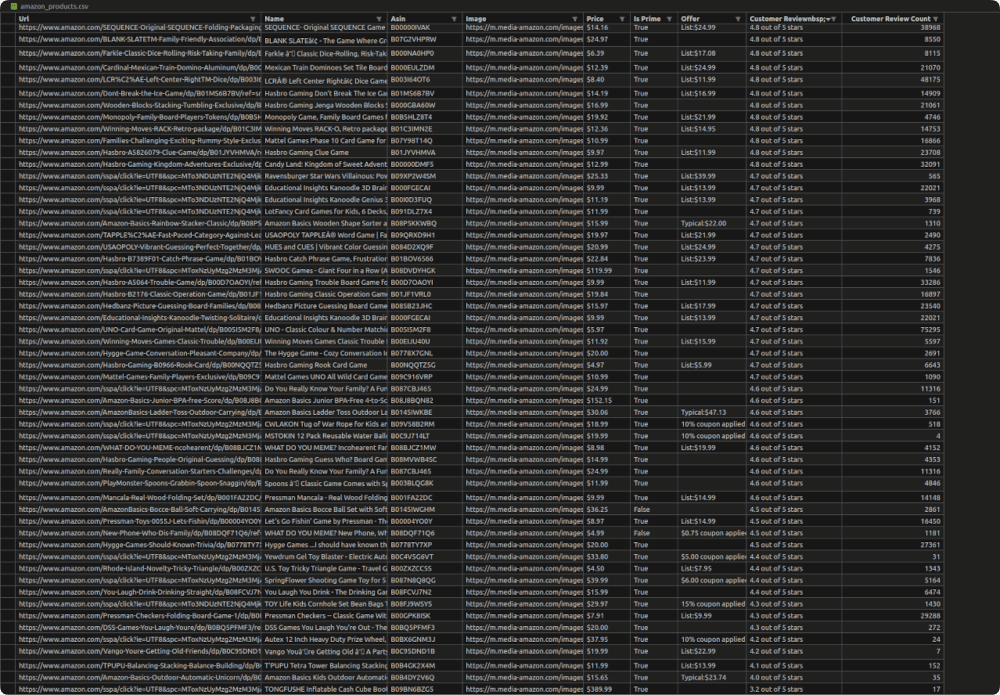
Handling Pagination
When scraping Amazon search pages, it’s crucial to handle pagination correctly to collect all the products you need. Crawlbase “amazon-serp” provides pagination information in the JSON response, including the current page, the next page, and the total number of pages.
1 | // Example |
As you can see, the “currentPage” indicates the page you are currently on, the “nextPage” shows the page number of the next set of results, and “totalPages” tells you how many pages are available in total.
To scrape all the products, you’ll want to iterate through these pages, sending requests with the appropriate page number appended to the URL, just as Amazon does:
- Page 1: https://www.amazon.com/s?k=games&page=1
- Page 2: https://www.amazon.com/s?k=games&page=2
- … So, on until the last page.
Lets update the example code to handle pagination and scrape all the products:
1 | from crawlbase import CrawlingAPI |
In this code section, we initiate the web scraping process. First, we define the Amazon search URL we want to scrape. Then, the code checks for pagination information on the initial page. If pagination is present, meaning there are multiple result pages, the code iterates through subsequent pages to scrape additional product data.
Finally, the extracted data is organized into a Pandas data-frame, allowing easy data manipulation, and the data-frame is saved to a CSV file. This code ensures you can gather a comprehensive dataset of Amazon products from search results, even if they span multiple pages.
amazon_products.csv Preview:
5. Final Thoughts
As professionals further engage in web scraping activities, adhering to ethical and technical standards remains paramount. Compliance with a website’s terms of service and robots.txt guidelines is mandatory. Moreover, ensure web scraping is used for legitimate, constructive purposes. With the knowledge acquired from this guide, professionals are well-equipped to harness the extensive data potential that Amazon’s product listings offer, driving analytical and business outcomes.
Sign up on Crawlbase and get 1,000 free credits
6. Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Can I scrape Amazon search pages for personal research or analysis?
Scraping Amazon search pages for personal research or analysis is generally acceptable, provided you comply with Amazon’s terms of service and respect their website’s rules. However, it’s essential to be mindful of the volume of requests you send to the website, as excessive scraping can lead to IP blocking or other measures to prevent scraping. To tackle this problem, you can consider using a Crawlbase Crawling API which allows you to scrape data from websites in a more structured and controlled manner, helping you avoid potential issues associated with excessive requests. This approach can enable you to conduct research and analysis while staying within the bounds of Amazon’s policies.
Q: Are there any rate limitations or CAPTCHAs when scraping Amazon?
Yes, Amazon employs rate limiting and CAPTCHAs to protect its website from excessive or automated access. When scraping Amazon, it’s essential to send requests at a reasonable rate and implement mechanisms to handle CAPTCHAs if they are encountered. Using a service like the Crawlbase Crawling API can help you navigate these challenges effectively.
Q: Can I scrape other e-commerce websites using similar techniques?
Yes, many e-commerce websites employ similar web scraping techniques, and the principles discussed in this guide can be applied to scrape data from other e-commerce platforms. However, keep in mind that each website may have its own policies and challenges, so it’s essential to review their terms of service and adapt your scraping approach accordingly.
Q: What are some common use cases for scraping Amazon search pages?
Common use cases for scraping Amazon search pages include market research, competitor analysis, pricing optimization, content aggregation for product review websites, and making informed investment decisions. Web scraping can provide valuable insights for e-commerce businesses, data analysts, researchers, and entrepreneurs.