Have you ever tried scraping real estate sites, only to hit a wall of CAPTCHA, rate limits, redirects, or IP bans? It’s like doing all the hard work and getting stuck at the finish line.
So, if you’re a founder building a rental data platform or a developer just trying to gather listings into Excel for insights, roadblocks like these can be deal-breakers.
But what if there was a cleaner way to extract accurate, structured property data without the usual headaches, and trusted by 70,000+ dev teams? Sounds like a fairy tale, right? Not exactly. Meet Crawlbase, the only tool you’ll ever need for AI-powered Web Scraping.
Here’s a short tutorial on how to automate real estate with Crawlbase:
Step-by-step Guide to Build a Real Estate Data Scraper
This guide shows how to scrape property listings from two real estate websites — Estately and Re/Max by using the Crawlbase Crawling API. We’ll extract data such as price, number of beds, number of baths, square footage, and address, then export it to an Excel sheet.
You don’t need to manage proxies, CAPTCHA, or JavaScript rendering. Crawlbase handles all that for you. So, without worrying, let’s get started.
1. Prerequisites
Before you begin, make sure you have:
- Node.js installed
- An IDE/Code Editor of your choice
- A Crawlbase Crawling API token → Get it here (1000 free requests)
- A basic understanding of JavaScript/Node (just enough to read functions)
2. Install Required Packages
Open your terminal and run:
1 | npm init -y |
These packages handle:
- Cheerio: To extract content from HTML, like jQuery
- ExcelJS: To write listings into an Excel file
- Crawlbase: To bypass CAPTCHA, blocks, and restrictions
3. Create the Script Files and Import Required Modules
First, create 2 new files for 2 different scripts called estately.js and remax.js. And this is how your project structure would look:
Then, import the required libraries by pasting the following at the top:
1 | const cheerio = require('cheerio'); |
These lines of code are required for both scripts, so don’t forget to add them.
Now, Let’s Look at What’s Different
Since we have two different scripts for two different real estate website listings, here is what we are gonna do:
- First, we will share the complete function code for each script
- Second, you will look at the code as a whole and try it
- Finally, we will walk through the Estately script step-by-step. Since both scripts follow a similar structure, understanding one will make the other a breeze.
1. How to Scrape Estately
What It Does:
- Visits Estately’s Cape Coral listings
- Extracts price, beds, baths, sqft, and address
- Saves everything to Excel
Add This Function:
1 | // Don’t forget to add the Shared Logic above |
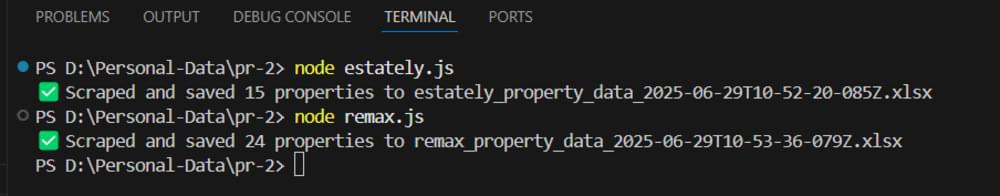
Now, open your terminal, run node estately.js, and see the results:
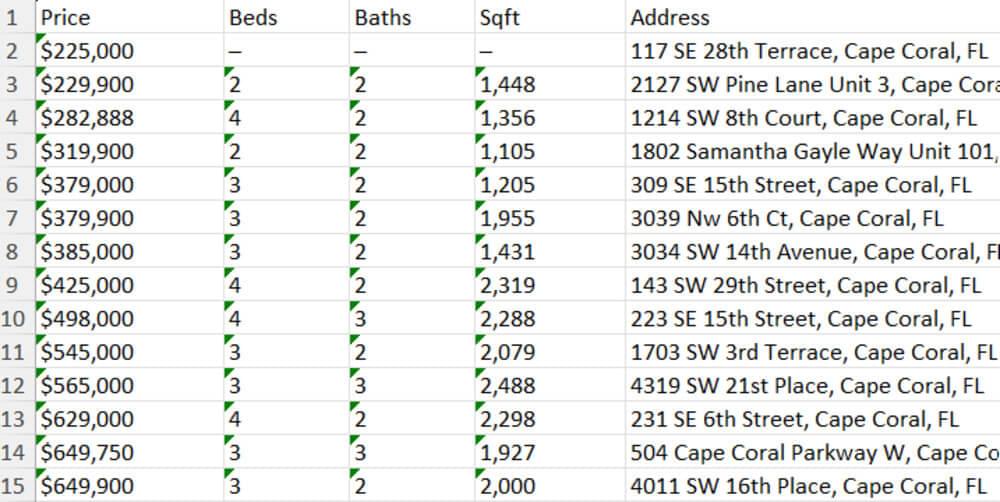
The result:
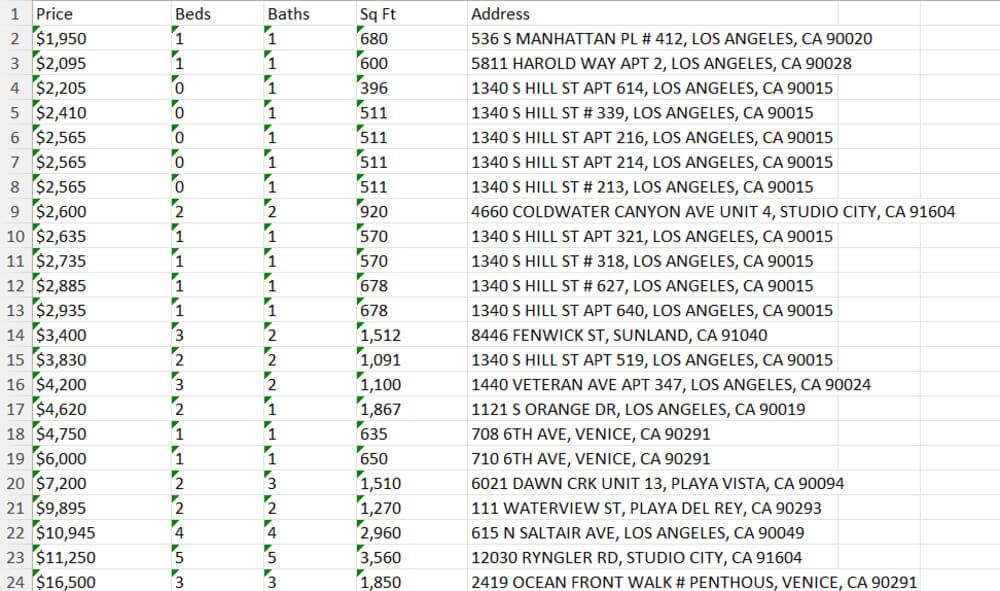
2. How to Scrape Remax
What It Does:
- Scrapes Re/Max rental listings in LA
- Extracts price, beds, baths, sqft, and address
- Sorts by price and saves to Excel
Add This Function:
1 | // Don’t forget to add the Shared logic above |
Now, open your terminal, run node remax.js, and see the results:
The results:
Step-by-Step Explanation for The Estately Script
1. Import Required Libraries
- Cheerio: Parses and extracts data from HTML (like jQuery).
- exceljs: Helps in creating and saving Excel files.
- CrawlingAPI: Comes from Crawlbase to fetch/render pages (especially dynamic ones).
1 | const cheerio = require('cheerio'); |
2. Start an Async IIFE
- An Immediately Invoked Function Expression (IIFE) is used to run asynchronous code right away.
tryandcatchhandles any runtime errors.
1 | (async () => { |
3. Set up Crawlbase API and Fetch Webpage
- Initializes
CrawlingAPIwith your API token. - Targets the Cape Coral, Florida listings on Estately.
response.bodycontains the HTML content of the page.
1 | const api = new CrawlingAPI({ token: 'YOUR TOKEN' }); |
4. Load HTML with Cheerio
- Loads HTML into Cheerio for DOM traversal:
1 | const $ = cheerio.load(html); |
5. Extract Property Data
- Finds all property cards using
div.result-item-details. - For each card:
- Extracts price, then removes $, ,, etc. for sorting
priceValue. - Gets beds, baths, and sqft from
<ul>><li>structure. - Extracts the address.
- Extracts price, then removes $, ,, etc. for sorting
- Pushes each structured property object to the
propertiesarray.
1 | const properties = []; |
6. Sort Properties by Price (Ascending)
- Ensures cheaper properties appear first.
1 | properties.sort((a, b) => a.priceValue - b.priceValue); |
7. Creates an Excel File and Add Data
- Initializes a new Excel workbook and worksheet:
1 | properties.sort((a, b) => a.priceValue - b.priceValue); |
- Defines column headers and widths for the Excel file:
1 | sheet.columns = [ |
- Adds each property object as a new row:
1 | properties.forEach((p) => sheet.addRow(p)); |
8. Save File with Timestamped Name
- Formats the current timestamp.
- Saves the file with a unique name.
1 | const timestamp = new Date().toISOString().replace(/[:.]/g, '-'); |
9. Success & Error Logging
- Success message:
1 | console.log(`✅ Scraped and saved ${properties.length} properties to ${filePath}`); |
- Logs any error if scraping fails:
1 | catch (error) { |
Final Thoughts
Scraping real estate data doesn’t have to be painful. With a combination of Crawlbase + Cheerio + ExcelJS, you get an easy, scalable flow that just works.
Instead of playing defense against CAPTCHA and bans, you should be able to build what you want to: value-driven tools, smart dashboards, or even simple reports.
If you’re looking for a way to reliably extract data from complex, protected sites, Crawlbase is the only web scraping tool you’ll ever need.