Yahoo Finance is one of the most popular platforms for tracking stock prices, financial news, and company data. With over 335 million monthly users, it’s a valuable source of structured and real-time financial data.
In this guide, you’ll learn how to extract data from Yahoo Finance using Python, along with best practices to avoid anti-bot measures.
TL;DR:
- Learn how to scrape Yahoo Finance using Python and Crawlbase Crawling API.
- Covers stock price, price change, and market timestamp extraction.
- Includes full sample code and Crawlbase integration tips.
Here’s a short video of how to scrape financial data from Yahoo Finance:
Table of Contents
1. Tools You Need (Python + Crawlbase)
2. Step-by-Step: How to Scrape Yahoo Finance Webpage
3. Extracting the Page Title with BeautifulSoup
4. Scraping Stock Prices from Yahoo Finance
5. Scraping Price Change (Up/Down) Indicators
6. Getting the Market Timestamp
7. Full Python Code: Yahoo Finance Scraper
8. Final Thoughts and Next Steps
9. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Tools You Need to Scrape Yahoo Finance (Python + Crawlbase)
Once Python is installed and you’ve figured out what IDE you prefer, it’s time to install the tools you need to scrape Yahoo Finance. The following commands will install the Crawlbase Python library and Beautifulsoup4
To install a package, simply open your command prompt (Windows) or terminal (macOS/Linux), create a directory where you want to store your Python code and use pip command to install the packages as shown below:
1 | pip install crawlbase |
2. Step-by-Step: How to Scrape Yahoo Finance Webpage
Now it’s time to write our code. We will first write a code to crawl the complete HTML source code of our target web page. In this step, we will be utilizing the Crawlbase package.
Start by opening your preferred text editor or IDE and create a new Python file. For the purpose of this guide, let’s create a file named scraper.py from your terminal/console:
1 | touch scraper.py |
For demonstration, we will be targeting this Yahoo finance page.
Copy the complete code below and read the explanation to understand each section:
1 | from crawlbase import CrawlingAPI |
Let’s try to execute the code. You can go to your console again and enter the command below:
1 | python scraper.py |
If successful, you will get a response similar to this:
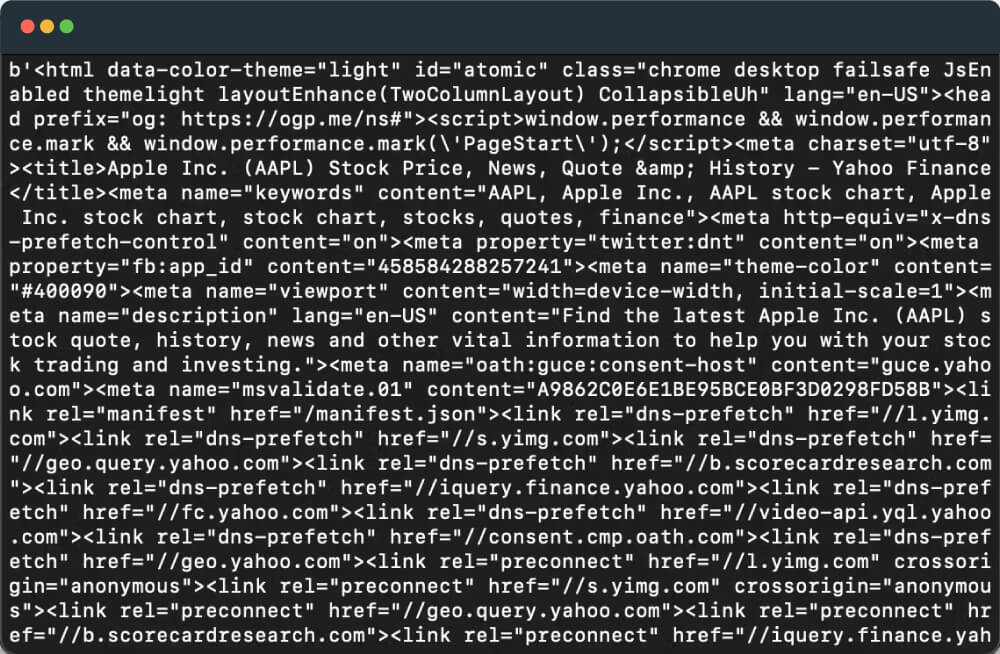
3. Extracting the Page Title with BeautifulSoup
For this section, we will now focus on scraping the content of the HTML source code we’ve obtained from crawling the Yahoo finance webpage. We should start by calling the Beautiful Soup library to parse the HTML and present it in JSON format.
1 | from crawlbase import CrawlingAPI |
Next we will need to look for the data we want to extract. Search for the Company name or the Title first. You will have to inspect the structure of the webpage using browser developer tools or viewing the page source by highlighting the Title, right-clicking, and selecting “Inspect” option.
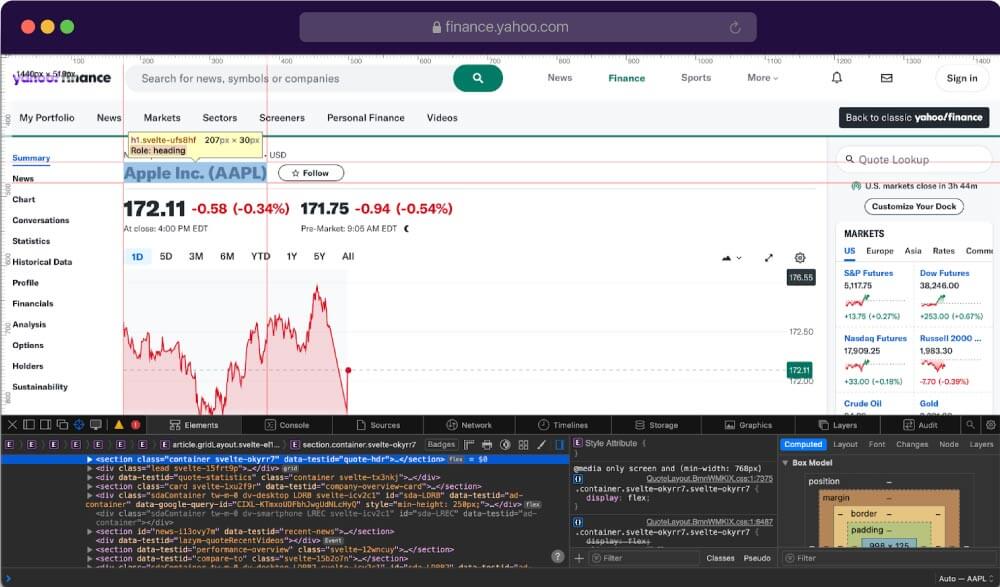
Once you have the line for the title element, simply utilize the BeautifulSoup selector to extract the data. Here’s how you can write the code:
1 | def scrape_data(response): |
The code starts by trying to parse the HTML content of the web page. It uses the BeautifulSoup constructor, passing the HTML content (response['body']) and the parser type ('html.parser').
Inside the try block, the function attempts to extract specific data from the parsed HTML. It tries to find an <h1> element with a class name 'svelte-ufs8hf' using the select_one method provided by Beautiful Soup.
Once the element is found, it retrieves the text content of the <h1> element and assigns it to the variable title. If the <h1> element is not found, title is set to None.
In case of an error, it prints an error message to the console and returns an empty dictionary as a fallback.
4. Scraping Stock Prices from Yahoo Finance
The next relevant data we want to extract for the Yahoo finance webpage is the most recent trading price of a financial asset or simply the Price. Start by highlighting the price and inspecting it like shown in the image below:
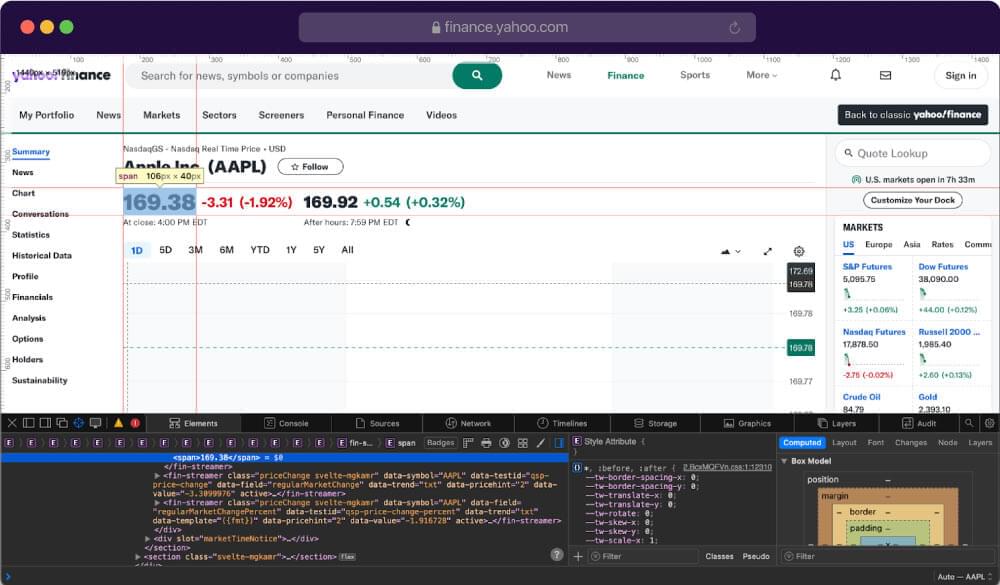
Write the code to extract the Price element:
1 | def scrape_data(response): |
Same as the code above, this will allow us to extract the specific element from the complete HTML source code and remove any irrelevant data for our project.
5. Scraping Price Change (Up/Down) Indicators
Our next target data would be the Price change. This value represents the change in the price of a financial asset, such as a stock, from its previous close.
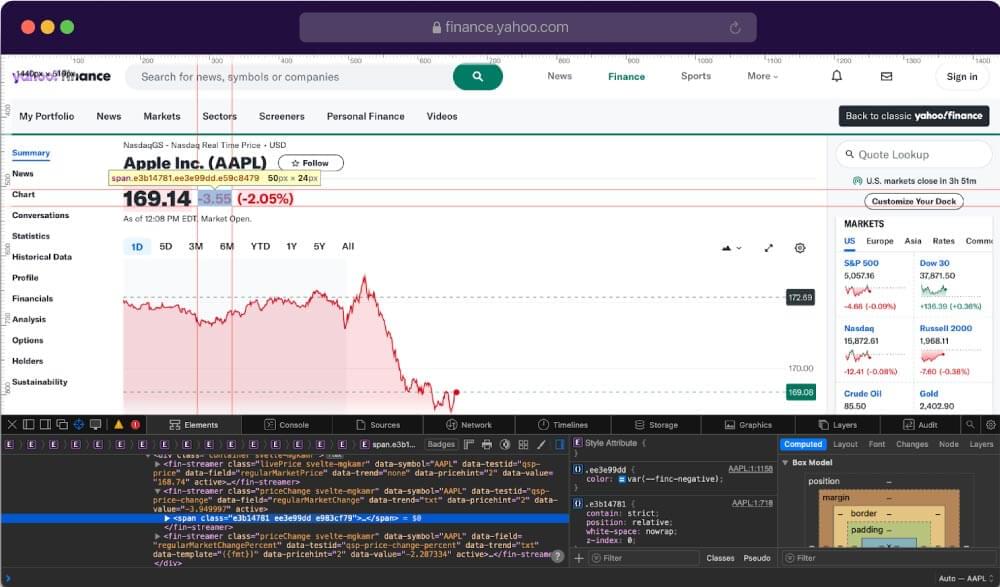
Again, simply highlight the change price and get the appropriate selector for the element.
1 | def scrape_data(response): |
6. Getting the Market Timestamp
Lastly, we will also scrape the Market Timestamp. It refers to the specific date on which the prices are calculated. For example, if you see “At close” followed by the date “April 19, 2024,” it means that the information being provided pertains to the closing price of the asset on April 19, 2024.
Also note that if it shows “Market Open”, this indicates that the price being displayed is the price at which the asset started trading when the market opened.
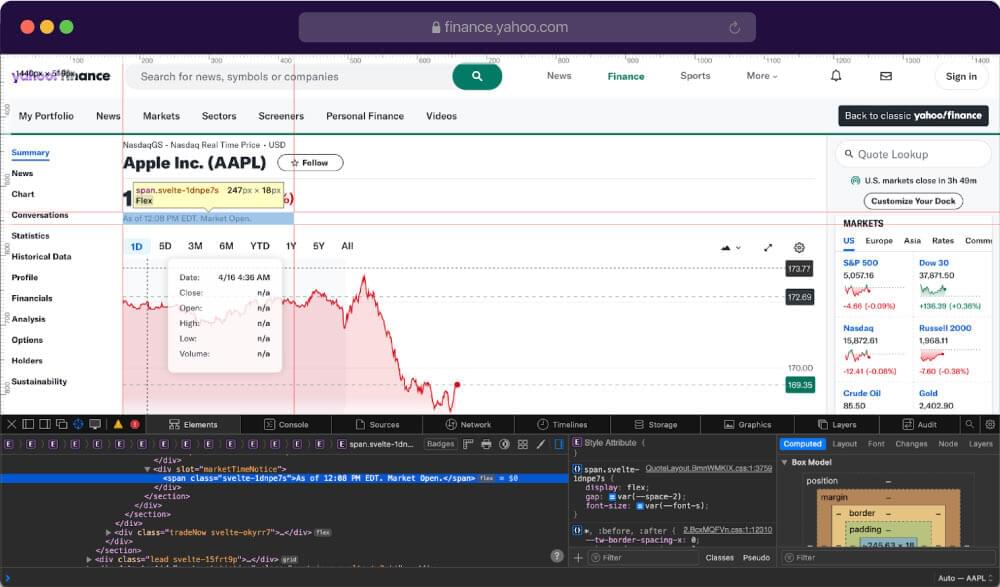
Highlight the data and go to inspect to get the associated selector. Let’s write the code once again to extract the data using BeautifulSoup.
1 | def scrape_data(response): |
7. Complete Python Code: Yahoo Finance Scraper
After writing the selector for each of our target data, it’s time to compile the code and bring our scraper to action. For your convenience, we’ve compiled the code below and add some lines to save the response as a JSON file. Feel free to copy and save it to your local machine:
1 | from crawlbase import CrawlingAPI |
Execute the code to get the response. Use the command below:
1 | python scraper.py |
If successful, it should provide a similar output as shown below:
1 | { |
There it is. The JSON format response will allow you to use the data effectively. Use it to analyze the stock market, compare prices, and so on. The choice is yours.
8. Final Thoughts and Next Steps
You’ve completed a comprehensive guide on how to efficiently build a scraper for Yahoo Finance using Python, Crawlbase API, and BeautifulSoup. You’ve learned how to extract clean and useful data from web pages and customize it for your projects or analysis.
The code shared in this guide is available for everyone interested. We encourage you to actively engage with it, as it can be useful for everyone including all sorts of developers, data scientist, or even for a curious learner. You are free to modify and tailor the code to suit your specific requirements. Tweak it for automation, scraping data from other websites, extract different types of information, or add new functions.
We recommend integrating with Crawlbase Crawling API, which handles IP rotation, CAPTCHAs, and rendering.
9. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Is web scraping legal for scraping data from Yahoo Finance?
Yes, web scraping itself is not inherently illegal, but it’s important to review and comply with the terms of service of the website you’re scraping. Yahoo Finance, may have specific terms and conditions regarding web scraping activities like many other websites. Make sure to familiarize yourself with these terms to avoid any legal issues.
How to scrape data from Yahoo finance?
- Identify the data to scrape and inspect the website
- Select a scraping tool or library to extract data from the web pages
- Use the chosen scraping tool to send an HTTP GET request to the target URL
- Parse the HTML content of the web page using the scraping tool’s parsing capabilities
- Depending on your needs, you can store the scraped data in a file, database, or data structure for later analysis or use it directly in your application.
What tools and libraries can I use for scraping Yahoo Finance?
There are several tools and libraries available for web scraping in Python, including BeautifulSoup, Scrapy, and Selenium. Additionally, you can utilize APIs such as Crawlbase API for easier access to web data. Choose the tool or library that best fits your project requirements and technical expertise.