Baidu, more commonly recognized as the “Chinese Google”, is the top search engine most people use in China. If you’re interested in things like market trends, SEO research, or just curious about what’s popular in China, getting data from Baidu is almost a must.
So in this blog, we’ll show you an easy way to scrape Baidu using Python and Crawlbase. Using such tools, building and managing proxies manually is no longer necessary; a simple script can do the job.
Start your sign up and get free credits to try Crawlbase now.
Table of Contents
- Scraping Baidu Search Results: Overview
- Setting Up Crawlbase and Coding Environment
- How to Crawl and Scrape Baidu
- Quick Tips to Scrape Baidu
- Frequently Asked Questions
Scraping Baidu Search Results: Overview
We’ll combine two main tools to extract data from Baidu, commonly referred to as the Chinese English Search Engine: Crawlbase and BeautifulSoup.
Crawlbase’s Crawling API enables you to avoid blocks when crawling websites. It employs all the necessary techniques, such as rotating IPs, handling CAPTCHAs, and simulating real browsers, to ensure the project’s success. This means you don’t need a complex scraper that mimics human behavior. You need to send the URL to Crawlbase and receive the complete HTML response.
Once we’ve got the HTML in hand, we’ll turn to BeautifulSoup for scraping. It’s a Python library that takes the mess out of parsing web pages, so finding and pulling out the exact info you want is quick and easy. You can pick out whatever tags or classes you need, almost like using familiar CSS selectors. This makes the script simple and easy to read for everyone.
We will focus on three key areas of the Baidu search results page with the scraper we’re going to build. Let’s look at this sample Baidu URL.
Open the page in your browser and inspect the following elements (right-click → Inspect):
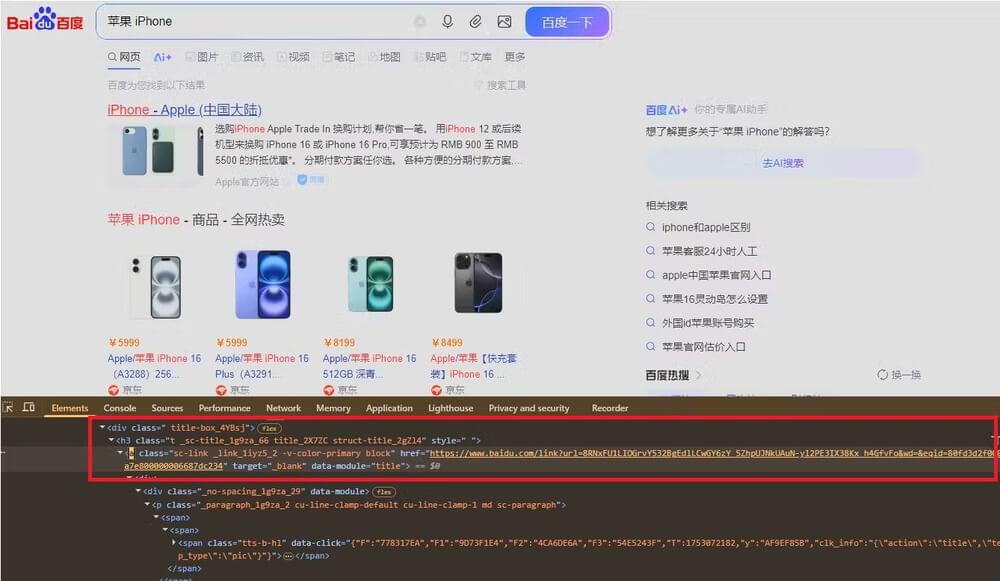
- Search Results: You can find this inside a
divwith the classtitle-box_4YBsj, followed by anh3tag with the classt.
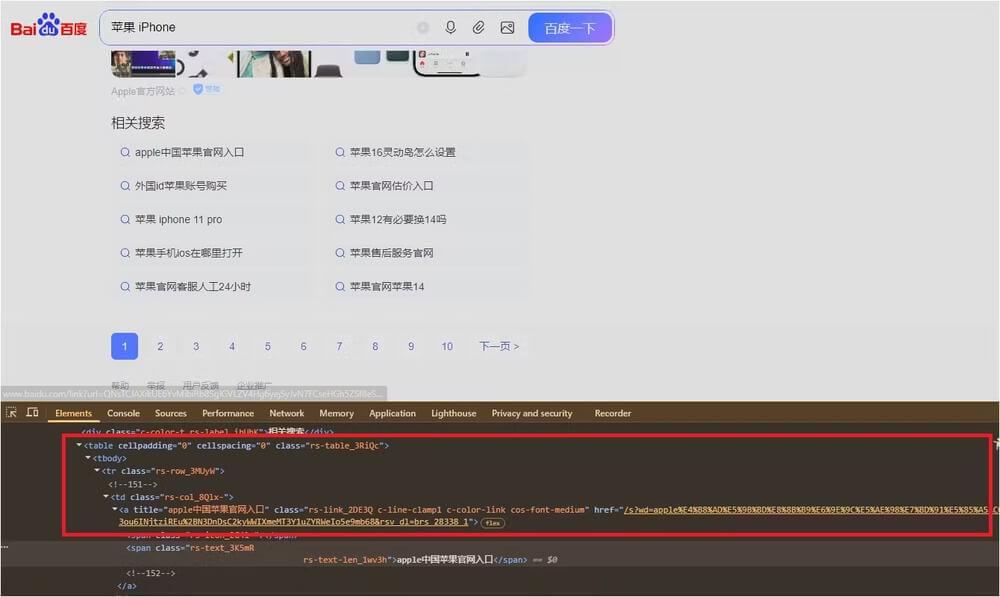
- Related Searches: These are found inside a
tablewith the classrs-table_3RiQc, navigating through itstrandtdtags to get the links.
- Pagination: To load more results, we increase the pn query parameter in the URL by multiples of 10 (like
pn=10,pn=20, etc.).
Setting Up Crawlbase and Coding Environment
- Go to Crawlbase to create an account and login.
- Your first 1,000 requests will be free of charge. If you want to get an extra 9,000 requests for free, simply add your billing details before consuming any of the free initial credits.
- Get your API key or the Normal request token. We’ll use it to crawl Baidu.
Next, set up your Python environment:
- Make sure Python 3 is installed.
- Open a terminal and install the required libraries:
1 | pip install requests beautifulsoup4 |
That’s it. You’re now ready to start writing the scraper.
How to Crawl and Scrape Baidu Search Results
Now your main tools are ready. Let’s have fun by creating a simple script to fetch the HTML using Crawlbase. It can be done with these steps:
Step 1: Handle blocks and CAPTCHAs with Crawlbase
Create a new file called crawling.py, and add the following code:
1 | from requests.exceptions import RequestException |
What This Script Does:
- Defines a
crawl()function that accepts a target URL. - Uses
requeststo send a GET request to the Crawlbase API. - Accepts your Normal Request token to authenticate the request. So don’t forget to change it.
- Checks that the original page returned a 200 OK status.
- Returns the full HTML content from the body of the response.
This script lets you fetch any public web page easily, while Crawlbase handles issues like blocking, CAPTCHAs, and rate limits for you.
Step 2: Scrape HTML with Beautifulsoup
We’ll use BeautifulSoup to extract the necessary data from the Baidu search results page for this step, which comes from the raw HTML obtained using Crawlbase.
So create a file called scraping.py and add the following code:
1 | from bs4 import BeautifulSoup |
What This Script Does:
- Parses the HTML using
BeautifulSoup. - Extracts the following data:
- The page’s
<title>tag. - The search query from the input field named “wd“.
- Search result titles and URLs from
div.title-box_4YBsj h3.t. - Related search links from
table.rs-table_3RiQc tr td a.
- The page’s
- Returns the data in a clean, structured format you can use or save.
Step 3: Combine Your Scripts
Now that we have both the crawling and scraping scripts ready, it’s time to put everything together and see the results.
Save the following to a file named main.py:
1 | from crawling import crawl |
What This Script Does:
- Uses your
crawl()function to fetch the HTML content of Baidu search results for the query “苹果 iPhone”. - Passes the HTML to
scrape_html()to extract structured data. - Converts the result into pretty-printed JSON and displays it in the console.
Step 4: Run the Main Script
From your terminal, run:
1 | python main.py |
You should see something like this:

This output confirms your crawler and scraper are working together successfully to turn raw HTML into clean, usable data.
Quick Tips for Scraping Baidu Search Results
Here are some quick tips to keep in mind as you continue building after setting up your Baidu search scraper with Python, Crawlbase, and BeautifulSoup:
- Crawlbase Rate Limits: Just be aware of the default rate limit of 20 requests per second to avoid 429 errors. If you need to send more requests than the default, you can contact Crawlbase customer support.
- 5XX pc_status codes: Any 5XX error codes are free of charge. If you encounter this type of error, it typically means that your URL is blocked, not responding, or currently unavailable. Luckily, you can easily retry these errors since it’s free of charge.
- Inspect HTML with DevTools: Always return to the HTML page and inspect the elements to check if there are any CSS class changes or if something breaks in your scraper. That’s a common problem, but a quick fix.
- Try different queries: Modify the Baidu search URL to test with other keywords and explore how the structure changes.
- Export your data: Write the output to a
.jsonor.csvfile usingjson.dump()orcsv.DictWriter()for later use.
If you haven’t already, sign up for Crawlbase to get your free API token and start exploring the web at scale, without getting blocked.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What is Crawlbase, and how does it help with web scraping Baidu?
Crawlbase is a platform mainly focused on web data collection. It handles the technical aspects of scraping, such as changing IP addresses, bypassing anti-bot protections, and returning the raw web page as clean HTML that you can easily use in your code. You don’t need to worry about running into common scraping roadblocks anymore.
Q: Can I scrape Baidu using Python?
Yes, you can. With requests and BeautifulSoup, you can fetch and work with search result pages. Crawlbase acts as a bridge, ensuring your requests are processed smoothly and preventing you from getting blocked.
Q: Why use BeautifulSoup for scraping Baidu search engine?
BeautifulSoup is designed for extracting data from web pages. Even if you’re starting out, it’s easy to work with. Also a popular choice for handling both tidy and messy HTML, like search results.
Q: Do I need to use JavaScript rendering to scrape Baidu?
Usually, Baidu’s main content loads without extra scripting. However, if you encounter a page that does require it, Crawlbase offers a JavaScript option to handle sites that necessitate a browser-style fetch.