n8n has been gaining a lot of attention because it lets anyone automate tasks easily. You can link services together, trigger actions, and build complete workflows through a clean visual interface. When you combine that with Crawlbase Web MCP, you get something even more powerful: a way to scrape real web pages and pass the data directly into AI models.
Crawlbase Web MCP acts as the connection point that allows your workflow to pull content from the web, convert it into a usable format, and feed it into whatever AI step comes next. This makes it ideal for research, monitoring competitors, collecting information at scale, and many other scraping tasks that usually require custom scripts.
Since many users want to know how to put these tools together, we will walk you through the setup and show you exactly how it works.
Before we begin, there are a few things you need to prepare.
What You Need to Set Up n8n with Crawlbase Web MCP
Make sure you have a few basics ready:
- n8n - The desktop app or n8n Cloud both work.
- A Crawlbase account - Sign up at Crawlbase to get your free API tokens.
- Node.js - Download and install Node.js to run the Crawlbase Web MCP server locally.
- ngrok (optional) - Only for n8n Cloud users who need their local server reachable online.
Once these are in place, you are ready to connect everything together.
How n8n Works With Crawlbase Through MCP
n8n uses MCP to talk to external tools. Instead of writing your own integration, you run the MCP server and n8n can call whatever functions that server exposes. In this case, the Crawlbase Web MCP server gives n8n access to Crawlbase’s crawling features.
The flow is pretty straightforward:
- the MCP Client Tool in n8n reaches out to the MCP server
- the Crawlbase Web MCP server provides the actual scraping functions
- your workflow receives the data and passes it to your AI step
You do not have to deal with API headers or scripts. Once this is set, n8n sends the request and Crawlbase returns the data you asked for.
Ready? Let’s begin.
Step 1: Install and Start the Crawlbase Web MCP Server
You’ll need to have the MCP server running, since it’s responsible for making the crawling features available to n8n. So, open your Node.js terminal and install the project:
1 | git clone https://github.com/crawlbase/crawlbase-mcp |
Replace the placeholders below with your own tokens from the Crawlbase dashboard.
1 | CRAWLBASE_TOKEN=your_token CRAWLBASE_JS_TOKEN=your_js_token npm run start:http |
Here is what they do:
- CRAWLBASE_TOKEN is for standard crawling.
- CRAWLBASE_JS_TOKEN is for crawling pages that rely heavily on JavaScript.
Start the server. If everything is installed correctly, the server will be available at http://localhost:3000.
Keep this terminal window open because n8n will use this running server when you connect MCP later.
Note: If you want to review more configuration options, you can check the Crawlbase Web MCP documentation for HTTP Transport Mode.
Optional for n8n Cloud Users: Using ngrok
If you are on n8n Desktop, this part is not needed. Cloud users, however, need a public URL so n8n can reach the MCP server running on your local machine.
ngrok creates a secure tunnel from the internet to your local machine. Here is how to set it up:
- Install the ngrok CLI
- Link it to your ngrok account
- Start a tunnel to your MCP server:
1 | ngrok http 3000 |
You will get a link that looks something like:
1 | https://abcd1234.ngrok.io |
Use that as your endpoint in n8n.
Just a small reminder: since this exposes your MCP server online, avoid sharing the URL or your tokens.
Step 2: Connect n8n to the Crawlbase Web MCP Server
Open n8n and head to your workflow. Add an MCP Client Tool node next to your AI Agent node. This is the part that lets the AI Agent use the scraping tools from Crawlbase.
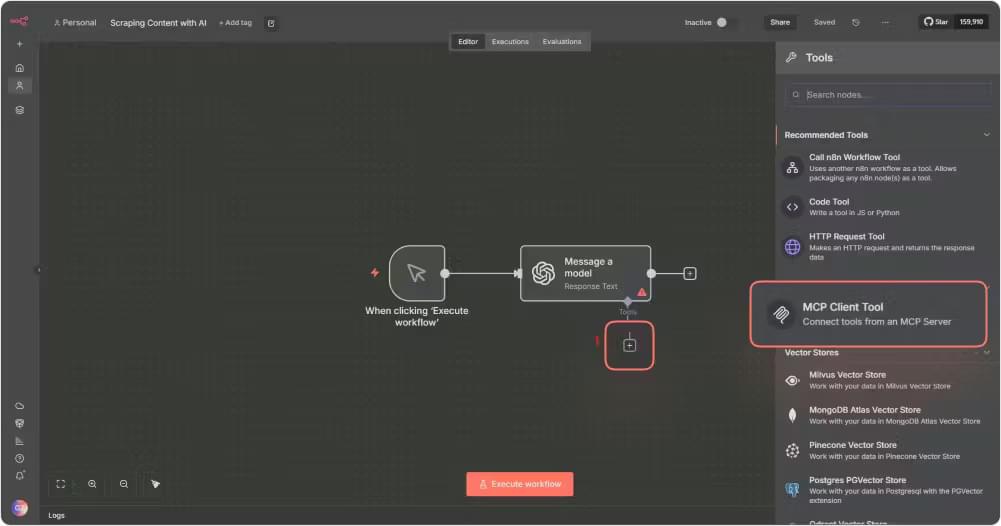
In the node settings:
- Endpoint
- Use
http://localhost:3000if you are working on n8n Desktop - Use your ngrok HTTPS URL if you are on n8n Cloud
- Use
- Server Transport: Choose HTTP Streamable
- Authentication: Select None, because your tokens were already set in Step 1
- Tools to Include: Choose All
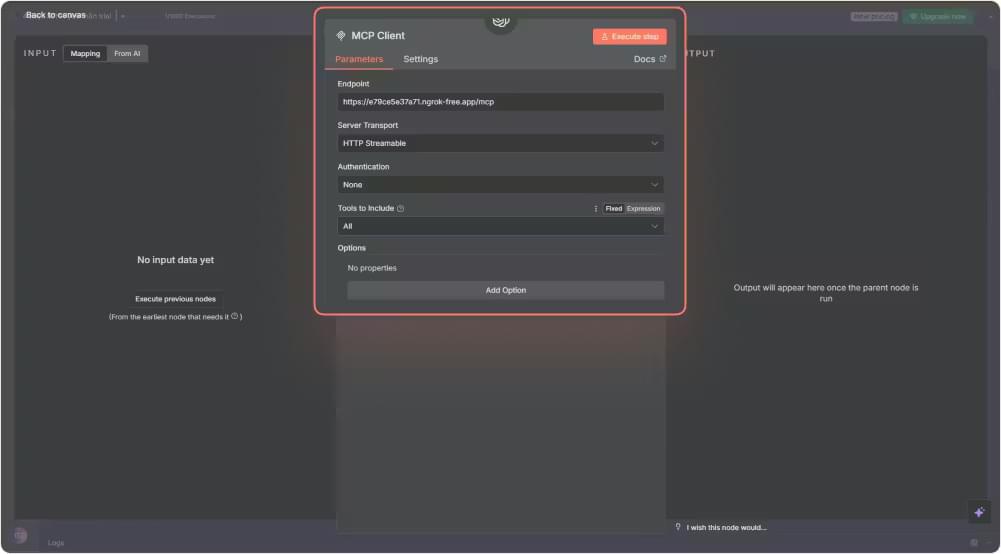
If the connection works, you will see tools like crawl, crawl_markdown, and crawl_screenshot appear inside the node.
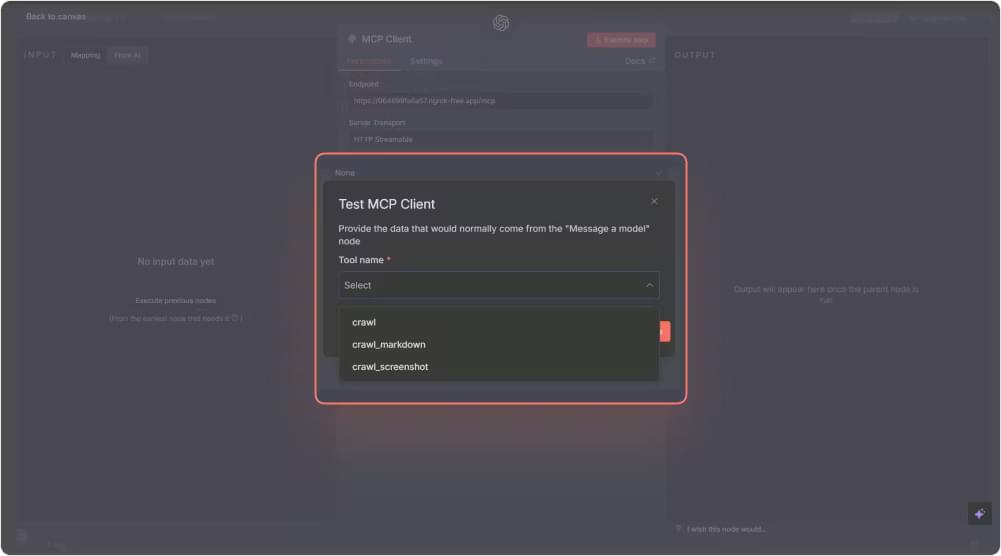
Your connection is now ready, and you can move on to building your first scraping workflow.
Step 3: Create Your First AI Scraping Workflow (No-code)
With everything connected, let’s build a simple workflow that pulls a webpage and creates a summary.
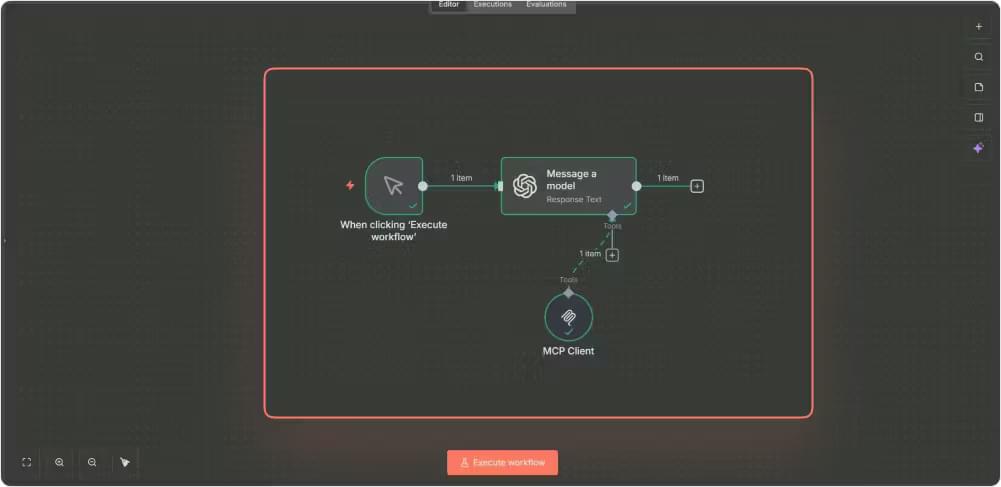
Your workflow will contain two main parts:
- An AI Agent node that already has access to the MCP Client Tool you configured earlier
- OpenAI Chat Model node that will generate the summary
Inside the AI Agent node, add a prompt that tells the AI what to do. For example:
1 | Crawl https://crawlbase.com/blog/best-web-scraper-api-2025 and summarize the article in 3 bullet points |
The workflow will trigger a crawl, collect the page content, and then pass it along to the model for summarizing.
Click Execute step on the AI Agent node to test your setup. Within a moment, you should see the summary appear in the output.
If you want to see what happened behind the scenes, open the workflow execution logs. You will see the crawl request, the data returned, and the markdown conversion step.
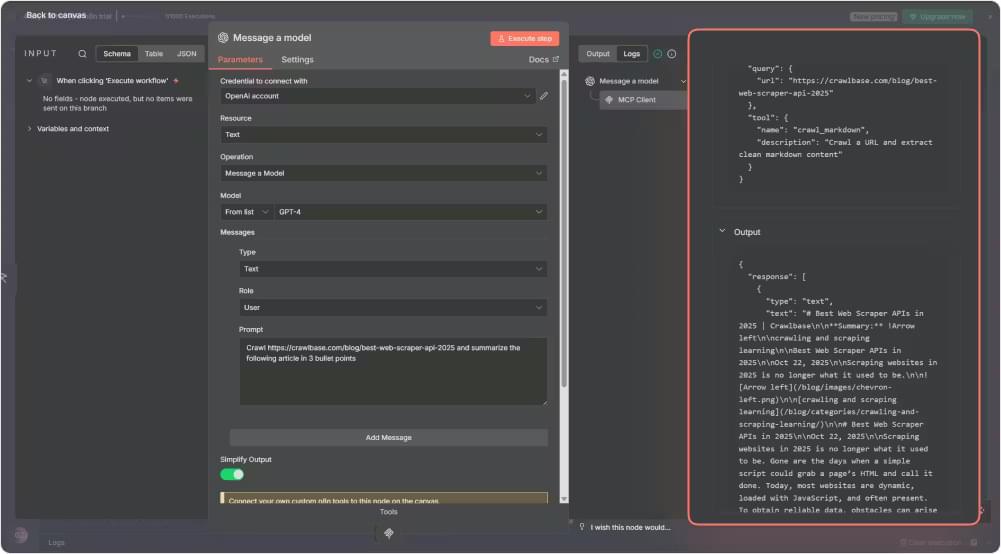
At this point, you have an automated loop where the AI Agent uses the crawl_markdown function, gathers the content, and produces a clean summary without any extra configuration.
Troubleshooting Tips for Connecting n8n to MCP Server
If something is not working as expected, these quick checks usually resolve the issue.
n8n cannot connect to the MCP server
- Make sure the MCP server is still running in your terminal
- Confirm the endpoint is correct, whether it is
http://localhost:3000or your ngrok URL - See if nothing on your system is blocking port 3000
Token or permission errors
- Verify your Crawlbase tokens in the dashboard
- Try copying the tokens again to avoid extra spaces or missing characters
- Ensure your account has enough credits to run requests
No tools appear in the MCP Client Tool node
- Confirm that Server Transport is set to HTTP Streamable
- Try to refresh the tool list inside n8n
- If nothing is loading, restart both n8n and the MCP server
Output is empty or looks incorrect
- Open the execution logs to see what was returned
- Test the workflow with a simpler URL
- Update your prompt so it clearly tells the AI to perform a crawl
Final Notes: Building More With n8n and Crawlbase Web MCP
By now, you have a working setup that lets n8n pull a page through Crawlbase Web MCP and hand the content to an AI model. It is a simple example, but once you see it run, it becomes obvious how much more you can do with the same idea.
Here are some ideas to try next:
- Scrape competitor pages on a schedule and have n8n drop short summaries into Slack
- Follow product prices across several sites and get notified when something changes
- Pull a handful of articles on the same topic and let AI create a quick overview
- Collect business details from directories and send them straight to a CRM
- Watch how certain pages change over time, especially for SEO work
If you want to go a bit deeper, you can chain multiple MCP tools in one workflow, add conditions so n8n handles each page differently, or store the scraped results in a place where you can compare them later. Scheduling also helps a lot, especially for recurring scrapes.
The nice thing about this setup is that you do not have to write code to build something useful. n8n handles the automation, Crawlbase does the crawling, and MCP keeps everything connected. Once you start experimenting, it becomes surprisingly easy to put together workflows that would normally require custom scripts.
If you want more inspiration, the n8n community has plenty of examples and discussions that can help you shape new ideas.
Create a Crawlbase account now and get your free credits to start building your own workflows today.