To build AI agent workflows with Crawlbase Web MCP, connect your AI agent (like n8n) to the Web MCP server, which handles web scraping automatically, bypassing JavaScript rendering, bot detection, and messy HTML. This setup enables your agent to fetch live website data, analyze it, and return structured answers without writing custom scraping code.
If you’ve worked with AI agents, you’ve likely hit a wall when they need real web data: sites block requests, content loads via JavaScript, or the HTML is too complex. The Crawlbase Web MCP server solves these problems by providing clean, structured data to your agent on demand. In this guide, we’ll walk through the complete setup.

How Crawlbase Web MCP Handles Web Scraping
At a high level, Crawlbase Web MCP enables AI agents to decide when and how to scrape web pages autonomously.
The workflow looks like this:
- The AI agent receives a task that includes a URL
- It determines whether scraping is required
- Crawlbase is invoked via MCP to fetch real page content
- The agent analyzes the extracted data
- A clean, structured result is returned
The key difference from traditional scraping workflows is that the decision to scrape is made by the AI agent, rather than being manually defined by you.
How to Build an AI Agent Web Scraping Setup with Crawlbase Web MCP
Building an AI agent web scraping workflow with Crawlbase Web MCP requires four core components:
- An AI agent platform (for example, n8n)
- The Crawlbase Web MCP server
- A language model (such as GPT-4)
- An MCP Client that connects everything
When a task containing a URL is received, the agent autonomously invokes Crawlbase to retrieve the page content, including JavaScript-rendered elements and bot-protected pages, and analyzes the response to produce structured output. This happens without writing custom scraping logic, request parameters, or parsing rules.
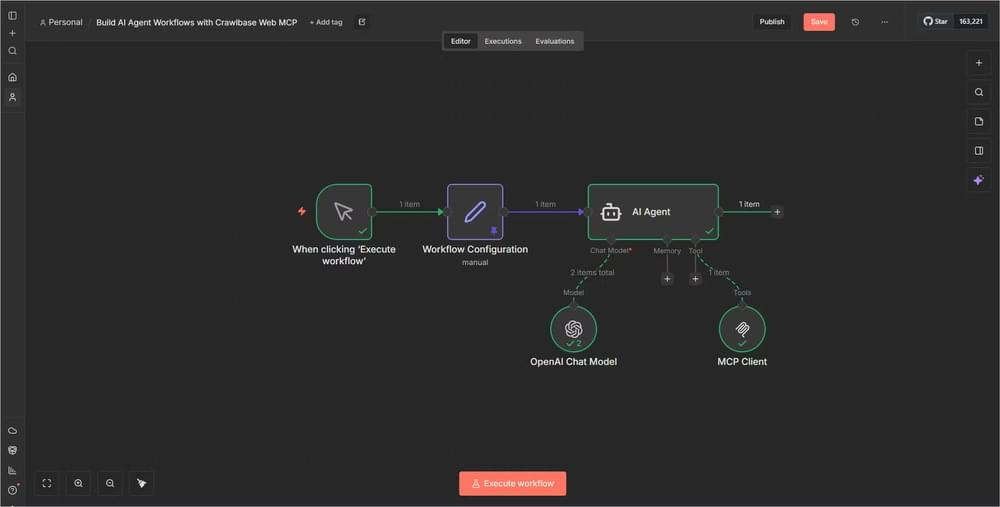
n8n Automated Agent Workflow Structure
In n8n, the workflow is implemented using five connected nodes:
- A Manual Trigger to start the workflow
- A Configuration Node to store the target URL and instructions
- The AI Agent Node for decision-making
- The OpenAI Chat Model for reasoning
- The MCP Client Tool that connects to Crawlbase’s scraping infrastructure
Once configured, the workflow is highly reusable. In most cases, you only need to change the URL and rerun the workflow; no changes to request settings or extraction logic are required.
Step-by-Step: Building the AI Scraping Workflow
If you’re new to n8n or want a quick refresher on how workflows and nodes work, the n8n documentation is a good place to start. Otherwise, let’s build our AI-powered web scraping workflow step by step.
Step 1: Create the base workflow
Start by creating a new automated agent workflow in n8n with these nodes:
- Manual Trigger - This will start the workflow on demand
- Workflow Configuration (Edit Fields) - To centralize parameters
- AI Agent - The brain of our operation
- OpenAI Chat Model - Powers the AI Agent
- MCP Client Tool - Connects to Crawlbase
You should end up with this setup:

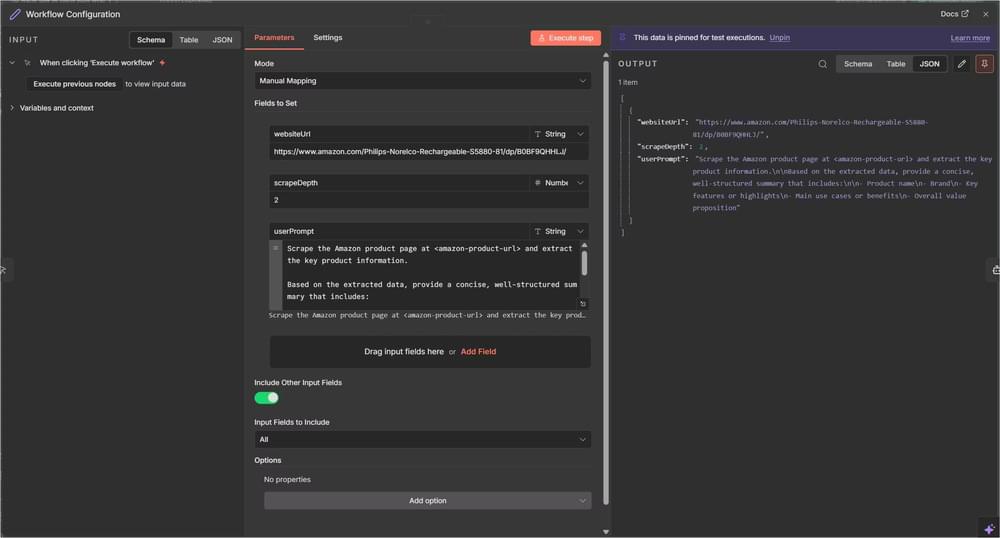
Step 2: Centralize Inputs in the Configuration Node
This node is where you define everything the agent needs.
Open your Workflow Configuration node and add the following fields:
websiteUrl(String): The URL to scrape(e.g., https://www.amazon.com/product-page)scrapeDepth(Number): How deep to crawl (default: 2)userPrompt(String): Instructions for the AI agent
Example prompt:
1 | Scrape the Amazon product page at <amazon-product-url> and extract the key product information. |
Make sure Include Other Fields is enabled so the data flows through.
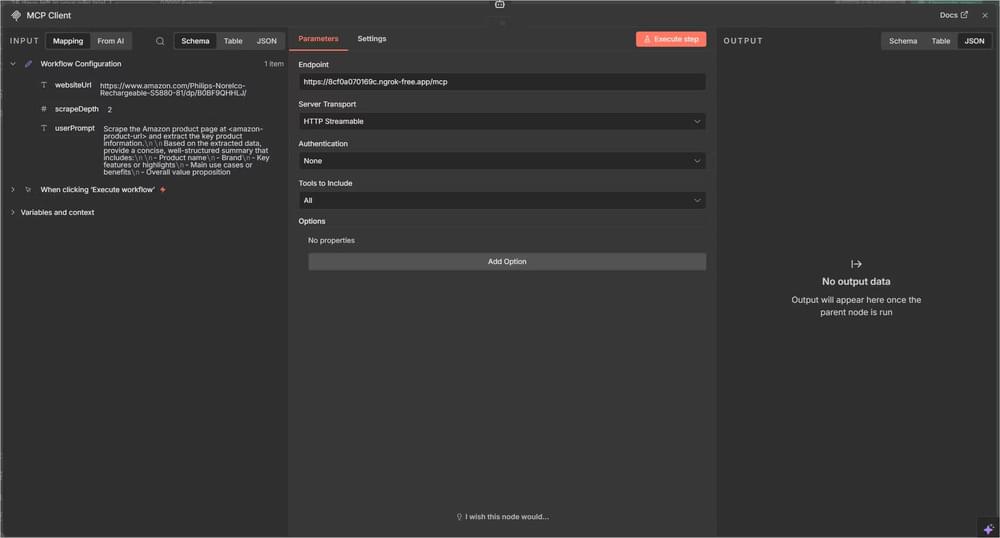
Step 3: Connect the MCP Client Tool
Open the MCP client node and configure it with the following:
- Endpoint URL: Your MCP server URL (e.g.,
https://your-ngrok-url.ngrok-free.app/mcp) - Transport:
httpStreamable - Authentication:
none(or configure based on your setup) - Include:
all(to expose all available tools)
This is what gives the agent access to Crawlbase.
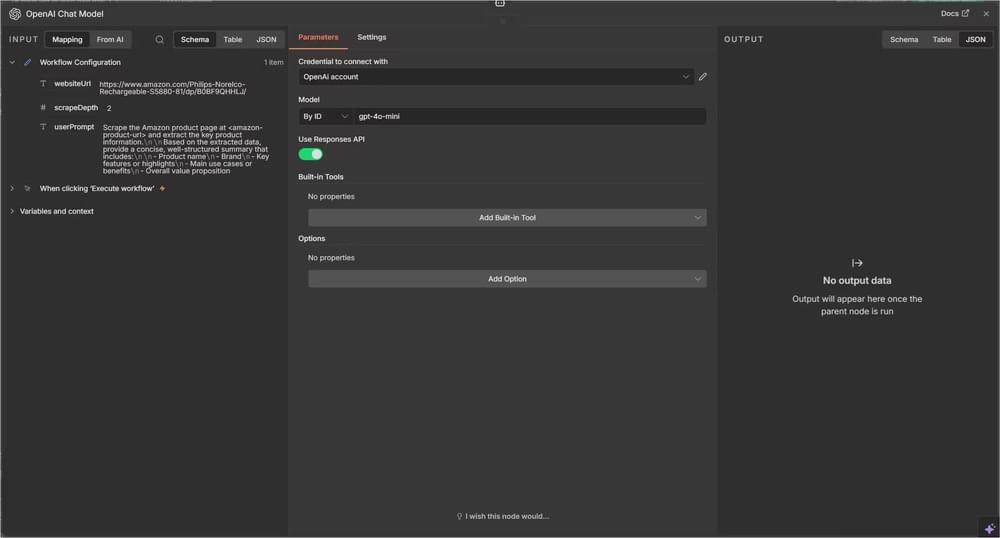
Step 4: Set up the Language Model
Now, open your OpenAI Chat Model node and set the following:
- Model:
gpt-4o-mini(good balance of speed and capability) - Credentials: Add your OpenAI API key
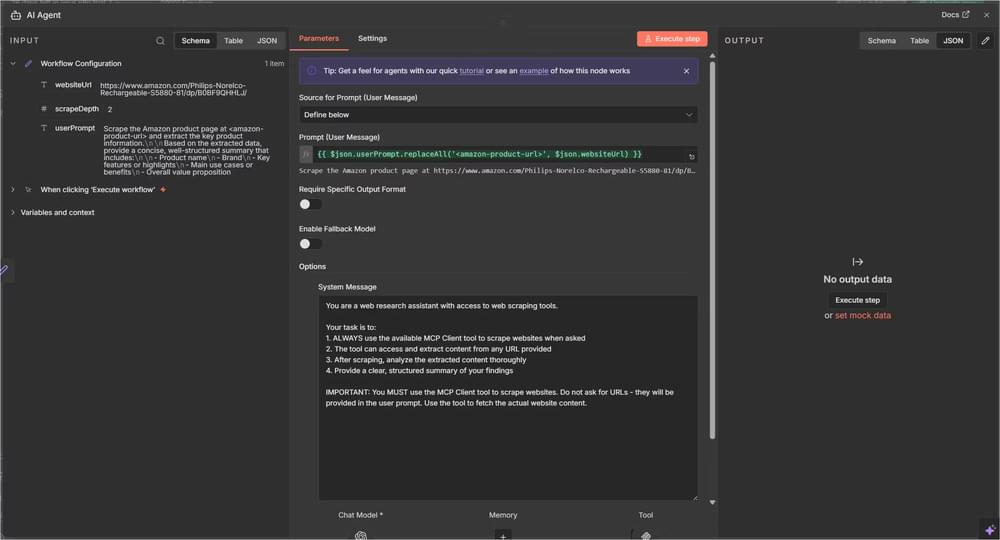
Step 5: Configure the AI Agent Node
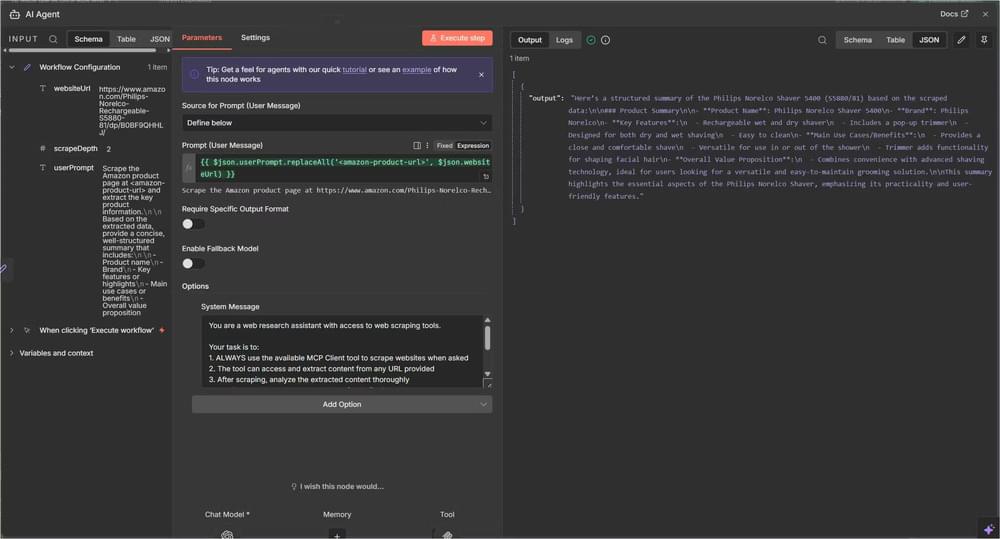
This is the core part of your workflow as the AI Agent handles the entire scraping and analysis process. So, go ahead and open that node and add the following:
Text Field (User Prompt):
1 | ={{ $json.userPrompt.replaceAll('<amazon-product-url>', $json.websiteUrl) }} |
This expression dynamically inserts the URL into your prompt.
System Message:
1 | You are a web research assistant with access to web scraping tools. |
This system message removes ambiguity. It tells the agent to use the scraping tool, follow the intended flow, and return results in a consistent format.
At this point, the workflow is ready to run.
Step 6: Execute Your Workflow
When you run this workflow, here’s what happens:
- Trigger Fires: The manual trigger starts the workflow
- Configuration Loads: Then, the Workflow Config node prepares all parameters
- AI Agent Receives Prompt: The agent gets the user prompt with the URL embedded
- Tool Selection: Then analyzes the prompt and decides to use the MCP Client tool
- Crawlbase Scrapes: The MCP Client calls Crawlbase’s API to scrape the website
- Data Returns: Crawlbase returns clean, structured markdown content
- AI Analyzes: The agent processes the scraped content
- Summary Generated: It produces a structured summary based on your requirements
At this point, the workflow is flexible enough to use in a lot of different scenarios. You might use it to check competitor pages from time to time, pull product details from e-commerce sites, gather notes from multiple sources for research, or keep track of news around topics you care about. It can also work for basic lead enrichment using public data, depending on what you need.
If you want to reuse or inspect the exact workflow shown here, the full setup and JSON file is available on GitHub and can be imported directly into n8n.
Why Use Crawlbase MCP Instead of n8n’s HTTP Request Node
You technically can, but in practice, it rarely holds up.
Most modern sites rely heavily on JavaScript, aggressive bot detection, and dynamic rendering. Fetching raw HTML often gives you incomplete or misleading content. You then end up layering retries, proxies, and custom parsing logic on top.
Crawlbase Web MCP removes that entire layer of complexity as it allows the AI agent to interact with the Crawling API which handles:
- JavaScript rendering
- Proxy rotation
- Anti-bot measures
- Retries and failures
- Clean, structured output
More importantly, this setup isn’t tied to a single site or request pattern. Since the agent is already working with Crawlbase directly, you can point it at different websites without reconfiguring API calls each time.
Best Practices for AI Agent Web Scraping
It’s a good idea to put a few simple checks in place early on. For example, adding basic error handling after the AI Agent makes it easier to notice when a scrape fails instead of missing it entirely. If you’re working through multiple URLs, spacing out the requests a bit using timeouts can help avoid issues. Saving the output somewhere like a database or even a spreadsheet also comes in handy later when you want to look back or do further analysis.
One more thing that helps a lot is adjusting prompts per site when needed. Trying to force one generic prompt across very different websites usually leads to weaker results.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
If you see a message like “none of your tools were used,” it usually means the agent wasn’t confident it should scrape anything. Making the system message more explicit and ensuring the URL is clearly included almost always resolves this issue.
For MCP connection issues, start with the basics. Check that the MCP server is running, confirm the endpoint is reachable, and test it directly with a simple curl request before digging deeper.
Next Steps: Deploying Your AI Agent Workflow
Instead of maintaining fragile, site-specific scrapers, you’re building a system where the AI decides what needs to be done, the tools handle the messy parts of the web, and the output stays clean and readable. When a site changes its layout, the whole workflow doesn’t immediately break. That’s the real long-term win.
From here, you can keep extending the same pattern. Add more MCP tools, schedule runs in n8n, experiment with multiple agents handling different tasks, or send results straight into your existing systems.
Combining n8n AI Agents with Crawlbase Web MCP gives you a practical way to work with live web data without constantly fighting scraping issues. Once you’ve built this workflow once, you’ll likely reuse the same structure again and again.
If you want to try it out, the next steps are straightforward: sign up for Crawlbase, clone the MCP server repository, import the workflow into n8n, and start experimenting.
FAQ: AI Agent Workflows with Crawlbase Web MCP
Q: Can this workflow scrape JavaScript-heavy sites?
A: Yes. Crawlbase Web MCP handles JavaScript rendering automatically, so the AI agent receives fully-rendered content without requiring Puppeteer or Selenium.
Q: How does Crawlbase Web MCP avoid bot detection?
A: Crawlbase uses proxy rotation, browser fingerprinting, and CAPTCHA solving to bypass anti-bot measures that would block standard HTTP requests.
Q: What AI models work with this setup?
A: You can connect Claude, Cursor, Windsurf, and other MCP-compatible AI Agents that support tool calling via n8n’s AI Agent node.