Imagine pulling a clean, ready-to-use dataset from almost any website without writing a single line of code. No dealing with HTML, no patching selectors, no stitching scripts together. You just describe what you want, and the agent handles the rest.
In this guide, you’ll see how AI changes web scraping from something you code to something you simply explain. Using Crawlbase Web Model Context Protocol (MCP), it takes care of everything else from loading the page to organizing the data into a clean format.
But before we jump into building your own AI scraper, let’s take a moment to set up the essentials below.

Tools Required For AI Web Scraping
- Cursor IDE - download it from the official Cursor website.
- Crawlbase account with API credentials - Create your account through the Crawlbase signup page.
- Crawlbase Web MCP - follow the official setup guide to configure it properly on your machine.
How the AI Web Scraping Setup Works
Everything runs on three main components that each handle a different part of the job.
Crawlbase’s Crawling API takes care of grabbing and loading the webpage. It deals with JavaScript-heavy pages, rotating proxies, CAPTCHA, and other blockers that normally get in the way of scraping. Then we have the Crawlbase Web MCP, which basically lets the AI talk to Crawlbase in a safe and controlled way. Finally, Cursor’s AI agents step in to read your instructions, pull the details you asked for, and shape the data into something clean and usable.
When these three pieces work together, you don’t have to touch HTML, build selectors, or write scraping logic. You simply describe what you need, and the system handles the rest.
Step-by-Step Guide to Building Your AI Web Scraper
Now that the overall setup makes sense, we can walk through the actual process. The steps are pretty simple, and once you try it once, the whole flow becomes second nature.
Step 1: Open Cursor
Install and run the Cursor IDE. Once it loads, this is basically where you’ll type whatever you want the agent to do.
Step 2: Enter Your Prompt
After that, just write out your prompt. For this example, we’re pulling info from eBay’s Best Selling Products page, so you can type something like what you’d normally ask a coworker: tell the agent to grab the data from that page and break it down for you.
1 | Crawl eBay's Best Selling Products page at https://www.ebay.com/str/bestsellingproducts |
When you see a prompt, just hit Approve to continue.
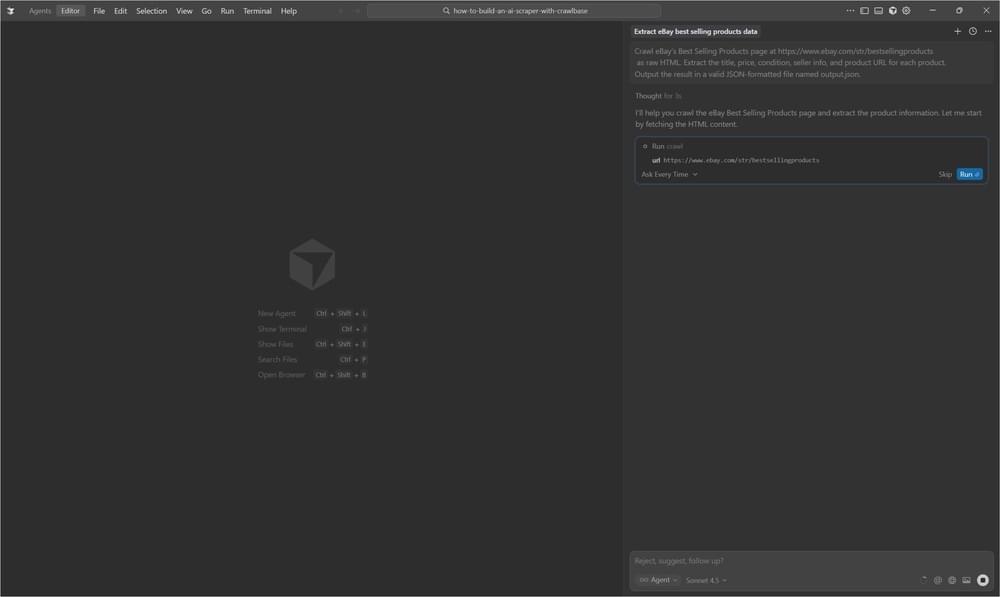
Step 3: Let the AI Agent Do Its Job
The AI takes over once you approve the request. In the background, it will:
- Ask Crawlbase Web MCP to load the page
- Looking through the HTML for each product on the list
- Pull the information you mentioned
- Build the output JSON file
You don’t have to write any parsing logic or touch the HTML yourself. The whole thing usually finishes in a few moments.
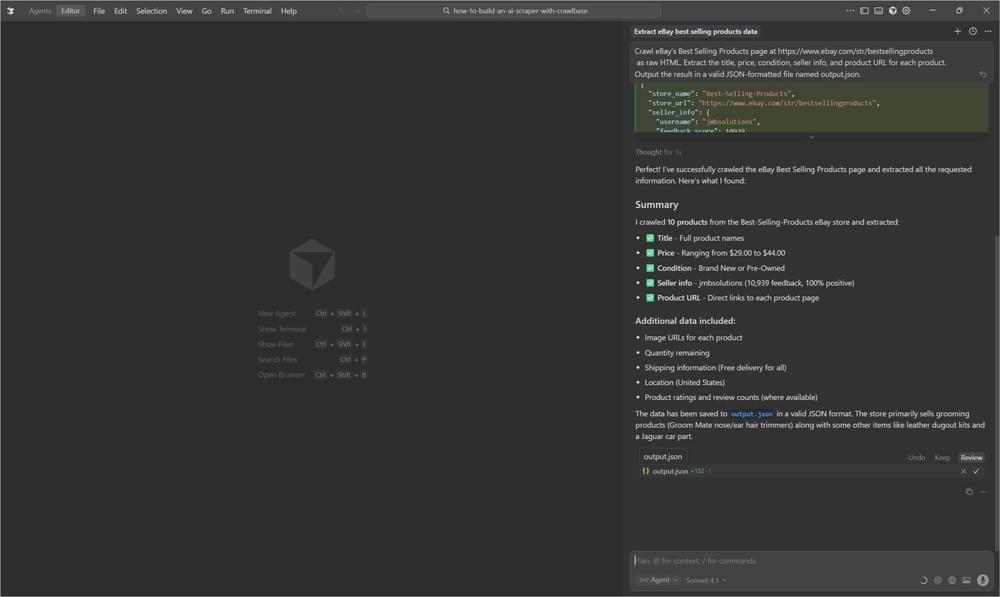
Step 4: Check the Results
After the run completes, you’ll see the generated JSON file. For the eBay example, the agent picked up ten products with the details you asked for. Everything is already cleaned up and ready to use.
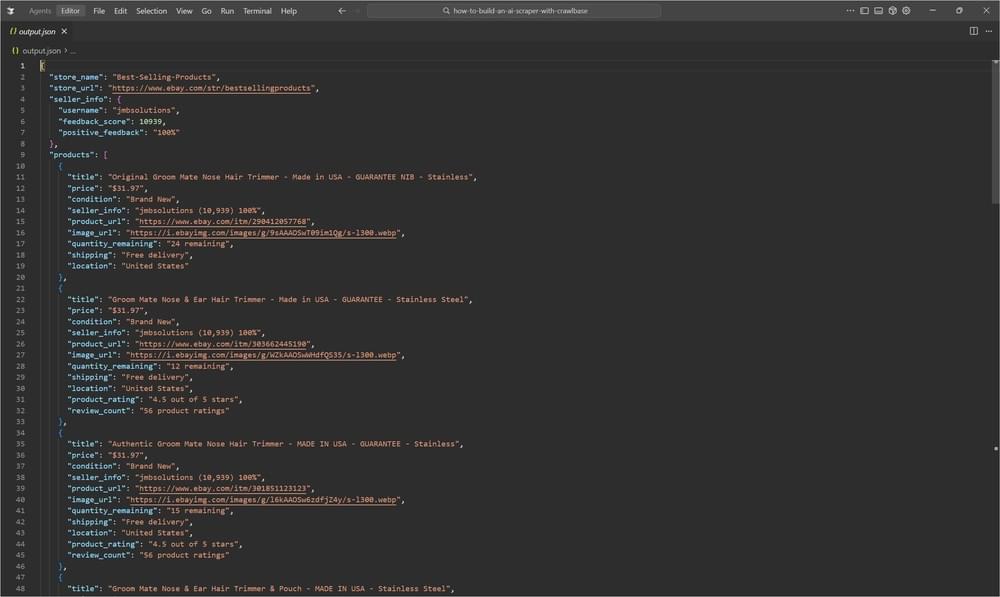
Best Practices for Getting Reliable AI Scraped Data
After you’ve gone through the workflow once or twice, you’ll start to notice that the quality of the output depends a lot on how you phrase your instructions. The agent is capable, but it still needs direction. A few simple habits can make a big difference in how clean your final dataset turns out.
Craft Clear Prompts
A general prompt won’t give you great results. It’s better to spell out exactly what you need instead of leaving it open-ended.
- Vague: “Get data from this website.”
- Clear: “Extract the product name, price, rating, and seller from each product card.”
Even small tweaks like this usually lead to much more predictable output.
Specify the Output Format
If you care about the data structure, say so up front. Something like:
1 | "Output as JSON with the keys: title (string), price (number), condition (string), url (string)" |
The agent tends to follow formatting rules closely when you state them plainly.
Plan for Missing or Odd Data
Real pages aren’t always tidy, so it helps to mention what to do when fields don’t exist. For example:
1 | "If a field is missing, set it to null. If a product is out of stock, still include it but add availability: false." |
This keeps your dataset consistent and saves you from cleaning everything manually later.
How AI Improves Web Scraping Efficiency
Zero-Code Solution
One of the first things people notice is how little you actually have to do. Normally, scraping means putting together chunks of code, testing selectors, and dealing with broken scripts. Here, you just describe the data you’re after and the agent figures out the rest.
Adaptive to Changes
If you’ve ever scraped a site that changes its layout, you know the pain of selectors breaking overnight. Since the agent isn’t tied to rigid CSS rules, it handles small shifts on a page much better. It looks at the content more naturally, which makes it less fragile when sites move things around.
Intelligent Extraction
The agent interprets the text instead of mindlessly extracting it. Prices are recognized even if the format isn’t consistent. Seller details get picked up even when they’re placed differently from listing to listing. It also collects extra bits of metadata when they’re useful and organizes everything into a cleaner structure.
Flexible Output
If you want the results in a different format, you don’t need to rework anything. You just tell the agent what you prefer. Ask for CSV instead of JSON, and it’ll give you CSV. Same prompt, no extra steps.
Complete Infrastructure
All the tricky parts of scraping are handled by Crawlbase in the background: rendering JavaScript-heavy pages, rotating proxies so you don’t get blocked, bypassing CAPTCHAs, managing sessions, and keeping everything stable. You don’t see most of this as it just works while your agent focuses on the data.
Use Cases for AI Web Scraping
As soon as you get comfortable with the workflow, you’ll probably start thinking of different places where it can fit into your projects. People use it for all sorts of tasks, but a few common patterns show up again and again.
Market Research
Teams often use it to keep an eye on competitors, like pricing, inventory, or just general movement across several online stores.
Price Monitoring
If you need regular price checks, this setup saves a ton of time. It can gather data automatically and alert you when something changes.
Product Discovery
Looking for trending items or bestsellers? The agent can go through product lists quickly and hand you a clear dataset to analyze.
Data Collection
Sometimes you simply need a clean table of information without spending hours copying and pasting. This workflow handles that well.
Content Aggregation
It’s also handy for building larger catalogs or collections when the data comes from multiple sources.
Pricing Difference Between AI and Traditional Scraping
Building your own scraper from scratch isn’t just a time sink; it can get expensive fast. By the time you factor in engineering hours and maintenance, the yearly cost stacks up.
- Traditional Scraping: roughly $8,000 to $25,000 in the first year
- AI-Powered Web Scraping: usually around $600 to $4,000 for the same period
Most teams end up saving somewhere between 70% and 90%, not to mention the time they get back.
Final Thoughts
Using AI with Crawlbase takes the complications out of web scraping. This approach brings a lot to the table. Lower costs, almost no maintenance, quicker setup, and the ability for anyone on the team (technical or not) to work with web data. It’s a practical choice for startups chasing competitive insights, analysts who need cleaner data pipelines, or businesses that want to scale their monitoring without adding engineering overhead.
If you want to see how smoothly this workflow fits into your projects, set up your Crawlbase account now and enable Crawlbase Web MCP. After that, open the Cursor and run the eBay example. It only takes a few minutes, and you’ll get a real feel for how much time this can save you. Once you’ve tried it, you can start scraping any site you need using the same process.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the best web scraper for AI automation?
Crawlbase Web MCP, combined with an LLM like Claude or GPT-4 enables automating web scraping. It handles complex and dynamic content while the LLMs interpret pages and extract what is needed.
What is the best AI web scraper for developers?
Crawlbase offers AI-powered extraction features like the Crawlbase Web MCP and Smart AI Proxy that automate and manage web scraping project needs efficiently.
How to make an AI web scraper:
- Pick your tools: Crawlbase Web MCP + Claude/GPT API
- Navigate to page: Use Crawlbase to load the URL
- Extract HTML: Get page content or specific elements
- Send to AI: Pass HTML to LLM with instructions on what to extract
- Parse response: LLM returns structured data (JSON)
- Handle pagination: Loop through pages as needed
Can AI be used for web scraping?
Yes, absolutely. AI enhances web scraping by:
- Understanding unstructured layouts without hardcoded selectors
- Adapting to site changes automatically
- Extracting semantic meaning (sentiment, categorization)
- Handling variations across similar pages
- Converting to structured data from natural text
AI doesn’t replace traditional scrapers but makes them smarter and more resilient to changes.